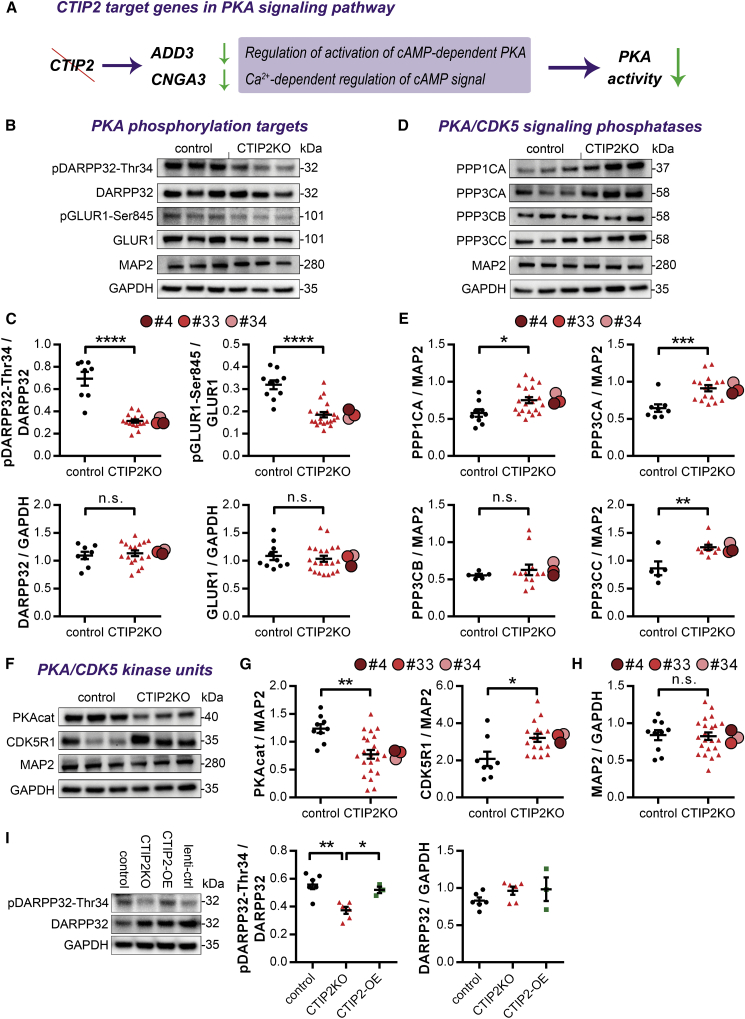
Figure 3.
PKA-Dependent DARPP32-Thr34 and GLUR1-Ser845 Phosphorylation Is Regulated by CTIP2 in MSNs
(A) Within the PKA signaling gene set, CTIP2 target genes (ADD3 and CNGA3) were significantly dysregulated and their change predicted to inhibit activation of cAMP-dependent PKA.
(B) Phosphorylation of PKA targets DARPP32-Thr34 and GLUR1-Ser845 is greatly reduced in CTIP2KO versus control MSNs.
(C) Quantification of (B) (left: n = 8, 17, 4; right: n = 10, 21, 4).
(D) Part of the PKA signaling pathway, levels of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) and 3 (PP3) catalytic subunits are significantly increased in CTIP2KO versus control MSNs.
(E) Quantification of (D) (from left, top row: n = 9, 20, 4; n = 8, 16, 3; bottom row: n = 5, 12, 3; n = 5, 10, 3).
(F) Compared with control cells, CTIP2KO MSNs contain reduced levels of PKA catalytic subunits (PKAcat) and increased levels of CDK5R1, a neuron-specific activator of CDK5.
(G) Quantification of (F) (from left: n = 9, 22, 4; n = 8, 16, 3).
(H) Quantification of MAP2 levels shows no differences between control and CTIP2KO MSN cultures (n = 10, 22, 4).
(I) Reduced phosphorylation of DARPP32-Thr34 in CTIP2KO no. 4 MSNs is rescued by restoring CTIP2 levels (n = 6, 6, 3).
(C, E, and G–I) One-way ANOVA; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each genotype, with the means for individual clones indicated by red-shaded circles beside CTIP2KO data.
See also Figures S1E and S4.