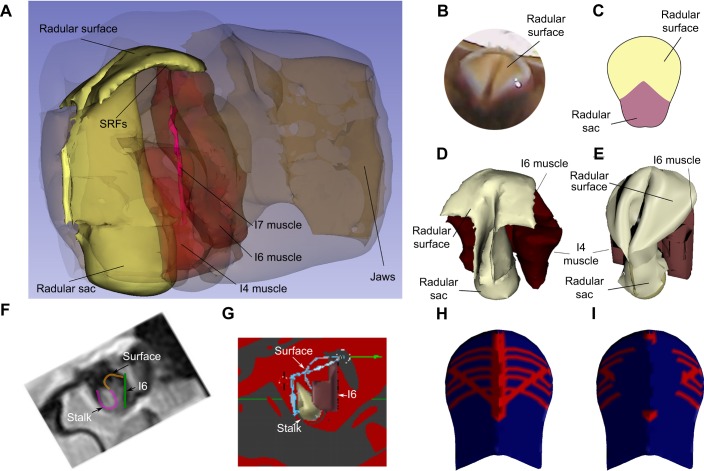
Fig. 3.
Soft radular surface model. (A) Reconstruction of the entire buccal mass based on high-spatial-resolution MRI provided initial resting positions for the muscles beneath the radular surface. (B) A dorsal view of the radular surface. (C) Schematic of the flattened radular surface. (D) Static image of the radular surface and underlying tissues extracted from the high-spatial-resolution MRI model shown in A. (E) Simplification of the structure of the I4/I6 complex (red mesh). (F) Location of structures during biting from a high-temporal-resolution MRI video frame. (G) Radular surface (blue line) is fitted to the model structures (based on MRI, F). (H) Vertex group representing SRFs (see text). (I) Lesion of sub-radular fibers (see Materials and Methods, ‘Model’).