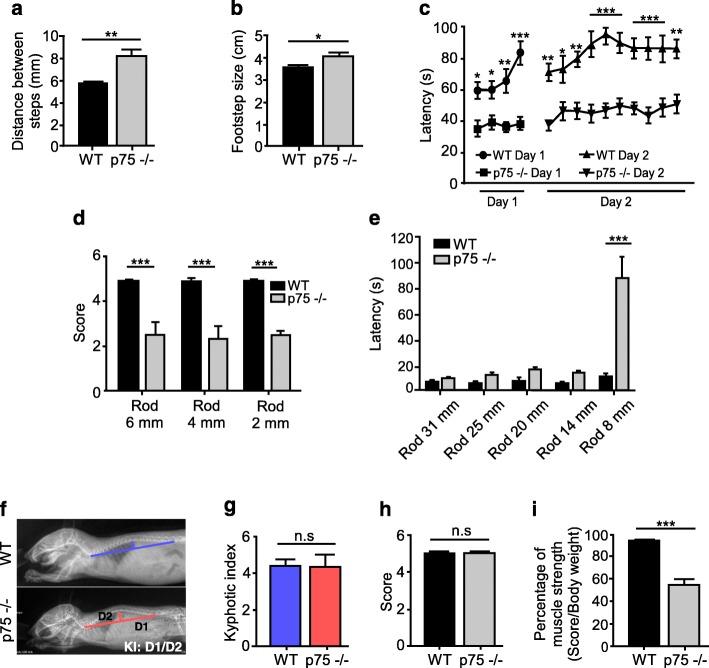
Fig. 4.
Altered motor performance and muscle strength in p75NTR−/− mice. a–e Young (2–4 months old) WT (n = 8) and p75NTR−/− (n = 8) mice were challenged in different motor tests. In the footprint test, p75NTR−/− mice displayed increased distance between steps (a) and increased distance between the fore and hind limbs steps (b) compared to WT controls. In the accelerating rotarod test, the latency time in two consecutive days was significantly decreased in p75NTR−/− mice compared to WT controls (c). Similarly, in the triple horizontal bar test (d) and the static bar test (e) p75NTR−/− mice had reduced scores and latency, respectively, compared to WT mice. f Representative X-ray images of WT and p75NTR−/− mice. The kyphotic index (KI) was calculated as the ratio between distances D1 and D2. g KI quantification show no differences between WT (n = 4) and p75NTR−/− (n = 3) mice. h–i Young (2–4 months old) WT and p75NTR−/− mice were challenged in two muscle strength tests. h In the Kondziela’s inverted screen test, no differences were detected between WT and p75NTR−/− mice. However, in the weights test (i), p75NTR−/− mice (n = 6) obtained a significantly impaired score compared to WT mice (n = 5). The results represent the mean ± SEM. n.s., non-significant, *p < 0.5; **p < 0.1; ***p < 0.01, unpaired t-test (a, b, g–i), or two-way ANOVA (c–e)