Fig. 4.
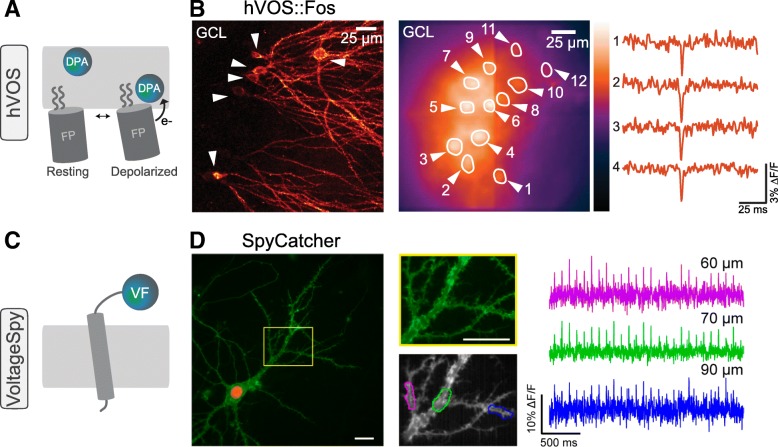
Chemogenetic voltage indicators. a Schematic representation of hVOS, consisting of a fluorescent protein anchored to the plasma membrane, combined with a non-fluorescent synthetic compound dipicrylamine (DPA), which serves as a voltage-sensitive FRET acceptor. b Cellular resolution voltage imaging with hVOS. Hippocampal slices from hVOS::Fos mouse expressing hVOS probe in granule cells in a Cre-Fos-dependent manner. Left: Fluorescence in brain sections after crossing Ai35-hVOS with Cre-Fos mice showing hVOS-expressing neurons in the granule cell layer of the hippocampus. Right: Response in four neurons in a hippocampal slice from an hVOS::Fos mouse to electrical stimulation. c Schematic representation of VoltageSpy, consisting of the expression of SpyCatcher on the cellular surface and the subsequent extracellular interaction with the VF dye. d Subcellular voltage imaging with VoltageSpy. Cultured hippocampal neurons co-expressing SpyCatcher and nuclear mCherry and labeled with VoltageSpy were captured at 500 Hz under widefield fluorescence microscopy. Left: VoltageSpy is shown in green and nuclear staining in red. Middle: Higher magnifications of selected dendritic regions. Scale bar 20 μm. Right: Voltage imaging in dendrites showing evoked action potentials in selected ROIs, coded by colors indicated in the panel. Images and traces modified with permission from [69] (b) and [82] (d)