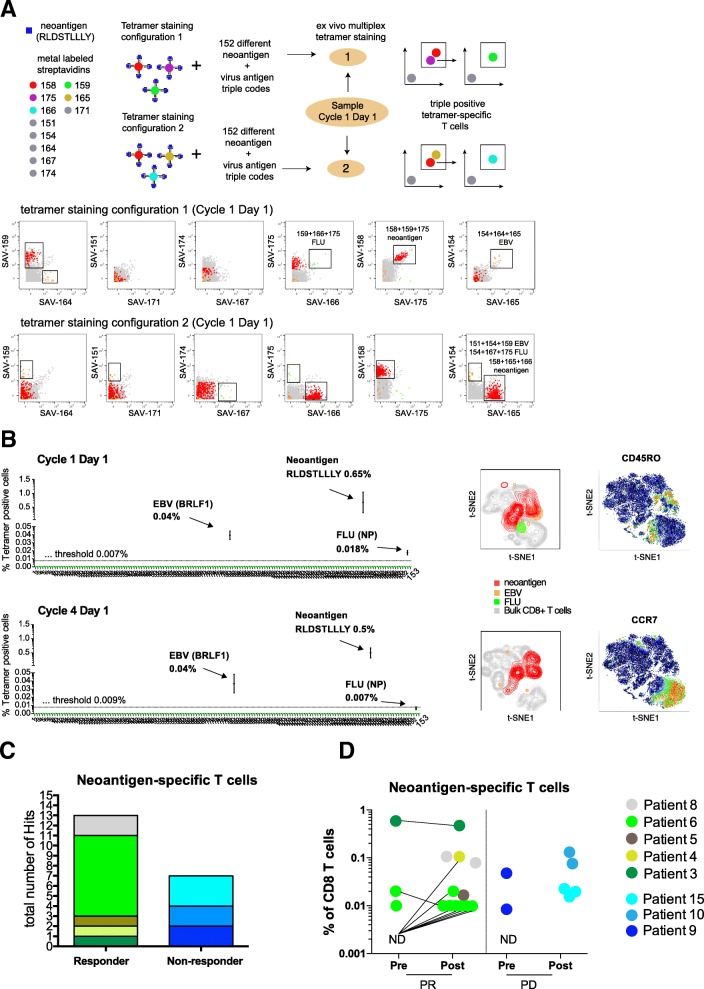
Fig. 2.
Neoantigen-specific T cells are enriched in patients responding to atezolizumab treatment. a Schematic overview of the multiplexed tetramer staining approach and corresponding example of identification of triple positive neoantigen and virus-specific T cells from a representative responder patient at baseline levels (cycle 1 day 1) in two staining configurations. Screening for antigen-specific CD8+ T cells was performed by using a mass cytometry-based multiplex triple coding tetramer staining approach assessing 153 candidate antigens, 126 neoantigens, and 30 cancer-unrelated control antigens for this patient. Each peptide-MHC was labelled with a unique combination of three heavy metal-streptavidin labels. b Same patient before (detection threshold 0.007%) and post atezolizumab treatment (detection threshold 0.009%). T cells specific for one neoantigen and two viral epitopes were identified based on the detection criteria set (see also Methods). t-SNE plots are based on the expression of all phenotypic markers. Relative expression levels of CCR7 and CD45RO are shown. c Total number of unique neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells (hits) detected from a total of 782 neoantigen candidates within the responders (n = 8 patients) and non-responders (n = 6 patients) groups. d Frequencies of all neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells detected within the responders (13 neoantigens) and non-responders (7 neoantigens) group pre- and post- atezolizumab treatment. The frequencies of T cells specific for neoantigens ranged from as low as 0.01% to as high as 0.65% of total CD8+ T cells. For patients where baseline sample was available but no antigen-specific T cells were detected are shown as N.D. Abbreviations: N.D., not detected; PR, responders; PD, non-responders