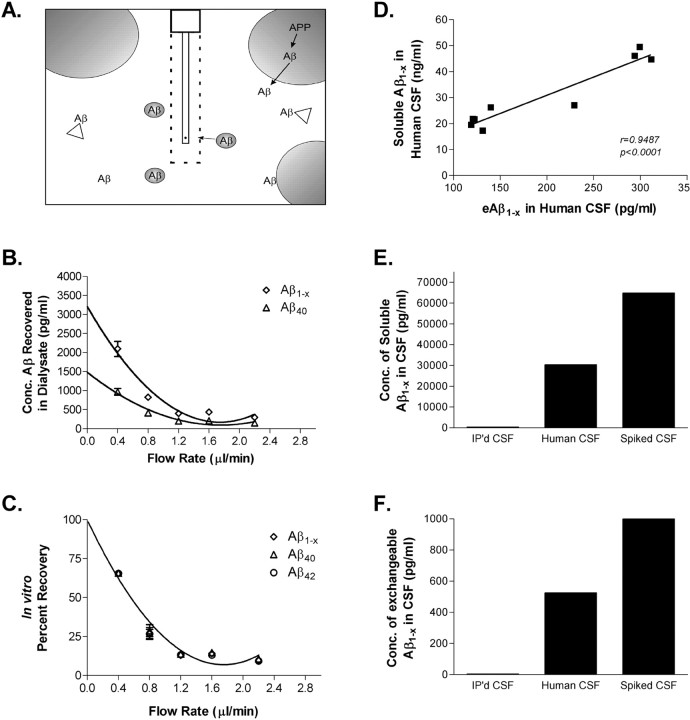
Figure 1.
In vitro microdialysis to measure Aβ. A, Diagram of exchangeable Aβ. Triangles represent potential Aβ binding molecules, e.g., apoE, clusterin, and α2M. Only highlighted Aβ molecules are of the appropriate size to pass through a 35 kDA MWCO membrane on the microdialysis probe. B, Interpolated zero flow method to quantify the pool of measurable Aβ1-x and Aβ40 within samples of human CSF (n = 4). At 2.2 μl/min, the percentage recovery of eAβ was 9.74 ± 1.53% (mean ± SEM). C, In vitro percentage recoveries for each Aβ species using the interpolated zero flow method. Each recovery point contains error bars and are overlapping for each species (n = 4). In vitro recovery of each Aβ species by microdialysis is the same. D, The concentration of eAβ and total soluble Aβ are highly correlated within a sample of human CSF (Pearson's r = 0.9487; p < 0.0001; n = 9). The mean concentrations of soluble Aβ1-x and eAβ1-x were 30.47 ± 4.23 ng/ml (mean ± SEM) and 196.2 ± 28.65pg/ml, respectively. E, F, Human CSF immunoprecipitated (IP'd) for Aβ has undetectable levels of total soluble Aβ and eAβ. Human CSF spiked with an amount of exogenous Aβ40 peptide expected to double Aβ concentration resulted in a 2.1-fold increase in total soluble Aβ and a 1.9-fold increase in eAβ.