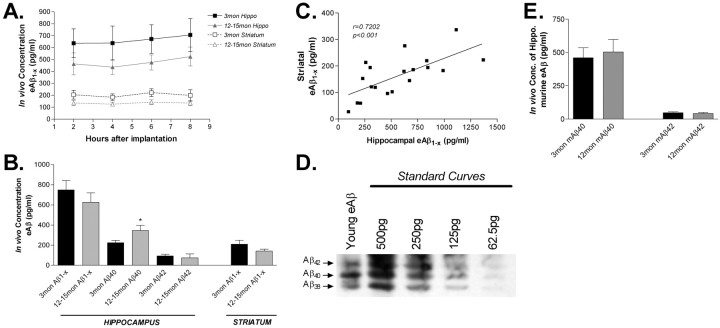
Figure 3.
In vivo concentration of eAβ in young and middle-aged PDAPP mice. A, ISF eAβ concentrations in hippocampus and striatum of 3- and 12- to 15-month-old PDAPP mice. Three-month-old mice have 727.7 ± 92.1 pg/ml (n = 21; mean ± SEM) and 207.9 ± 31.8 pg/ml (n = 6) of eAβ1-x in the hippocampus and striatum, respectively. Twelve- to 15-month-old mice have 626.4 ± 93.3 pg/ml (n = 21) and 142.1 ± 19.5 pg/ml (n = 13) of eAβ in those regions. B, The concentration of eAβ species in young and aged mice. The concentration of eAβ1-x does not change significantly with age. eAβ40 increases significantly in the hippocampus with age (p = 0.0429), whereas eAβ42 does not decrease (p = 0.6116). C, The concentration of eAβ1-x within the hippocampus and striatum are highly correlated (Pearson's r = 0.7202; p < 0.001; n = 19). D, A microdialysis sample was analyzed by acid- urea electrophoresis, followed by Western blot analysis to visualize the various Aβ species present. On the basis of the peptide standard curves, Aβ42,Aβ40, and Aβ38 represent 15.6, 31.6, and 52.8%, respectively, of the ISF Aβ detected. No other Aβ species were detected. This confirms that Aβ-CTV is a major pool of Aβ in the ISF and that Aβ38 is the predominant species. E, The concentration of endogenous murine ISF eAβ40 and eAβ42 was measured in 3-month-old (n = 6) and 12-month-old (n = 6) C57BL/6 mice. There was no change with age in the concentration of murine eAβ40 (p = 0.718) or eAβ42 (p = 0.609) in wild-type mice.