Figure 3.
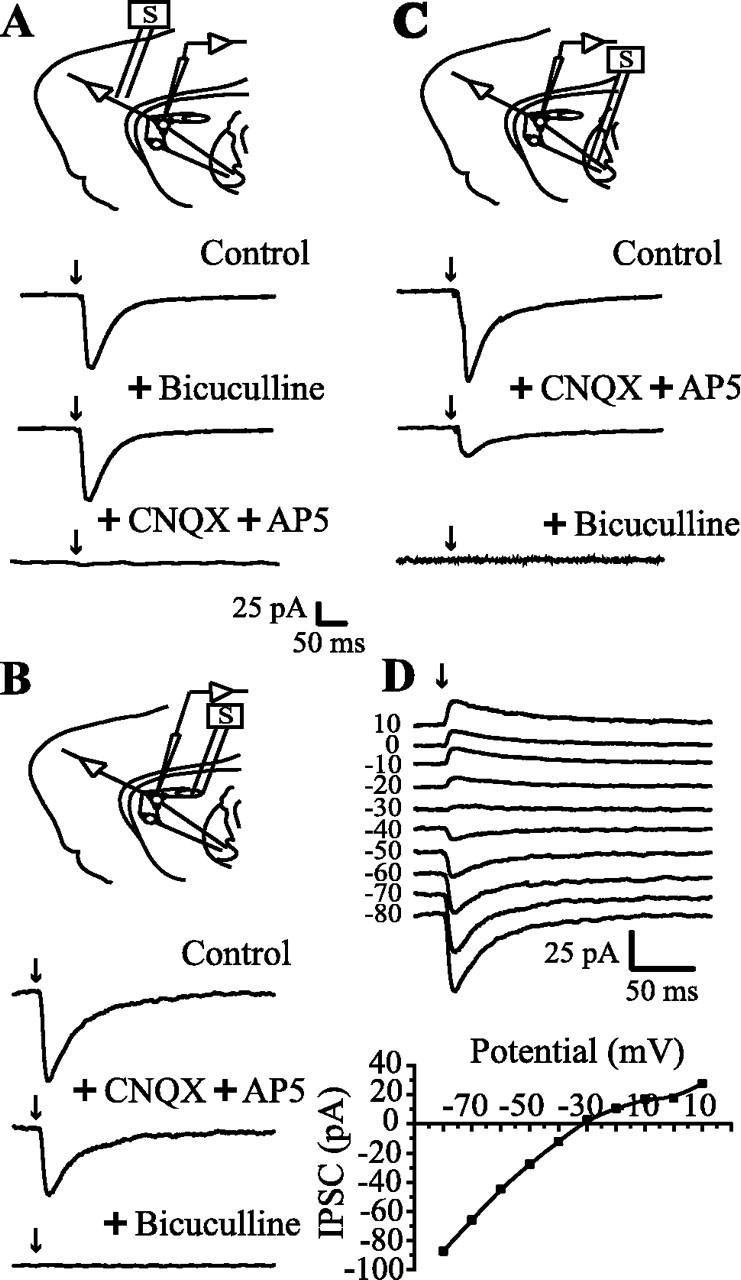
Evoked synaptic responses in a corticostriatal slice preparation. Top scheme in each frame illustrates the position of stimulating and recording electrodes; two medium spiny (round) and one local interneuron (ovoid) are symbolized. A, Synaptic currents were evoked by cortical stimulation (in this case, recordings are averages of 200 trials). Currents were blocked by CNQX (10 μm) plus AP5 (50 μm). No bicuculline-sensitive component was recorded with these stimulating conditions (1-4 V) (see Materials and Methods). B, Stimulation and recording in the neostriatum evoked synaptic currents that were only partially blocked by glutamatergic antagonists (CNQX and AP5 as before). Bicuculline (10 μm) blocked a GABAergic component. C, Stimulation in the GP (lesioned with ibotenic acid) and recording in the neostriatum. Axons from spiny cells were activated antidromically to turn on collaterals interconnecting spiny cells. Glutamatergic components (cortical projections also pass through GP) were blocked by CNQX plus AP5. A clear bicuculline-sensitive component was disclosed. D, Synaptic currents evoked by antidromic stimulation in the GP. Reversal potential was -28.7 ± 7 mV (n = 12), which was not significantly different from the chloride equilibrium potential (-30.5 mV).
