Figure 1.
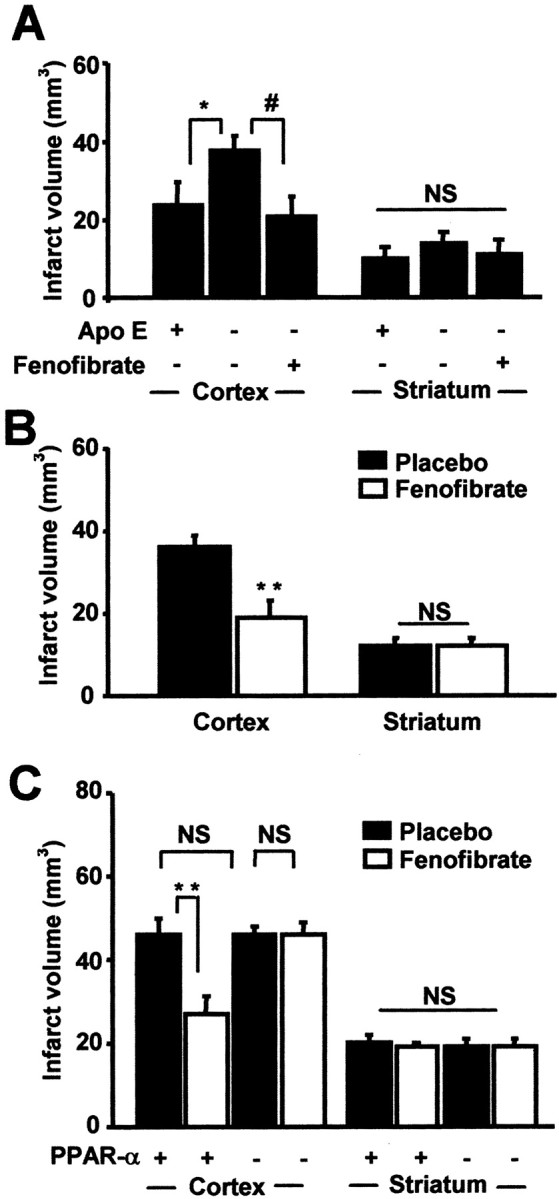
PPAR-α activation as a mechanism of fenofibrate-induced preventive neuroprotection. In A, Apo E-deficient mice were fed a diet containing 0.2% fenofibrate or placebo (n = 5 per group) for 14 d before a 60 min MCA occlusion was performed. In these conditions, the increased susceptibility to cerebral ischemia of Apo E-deficient mice and the neuroprotective effect of fenofibrate appear only in the cortical area. *, #p < 0.05. B, Using the same procedure, cortical infarct volumes in C57BL/6 wild-type mice (n = 6 per group) are reduced by 46% after fenofibrate treatment when striatal infarct volumes remain similar. **p < 0.01. C, Preventive neuroprotective effect of fenofibrate is confirmed in SV129 wild-type mice (n = 5 per group) submitted to a 90 min MCA occlusion. Such a neuroprotective effect is not reproduced in PPAR-α-deficient mice (n = 4 per group), just as PPAR-α deficiency does not induce any increase in cerebral infarct volumes. **p < 0.01. NS, Not significant.
