Figure 2.
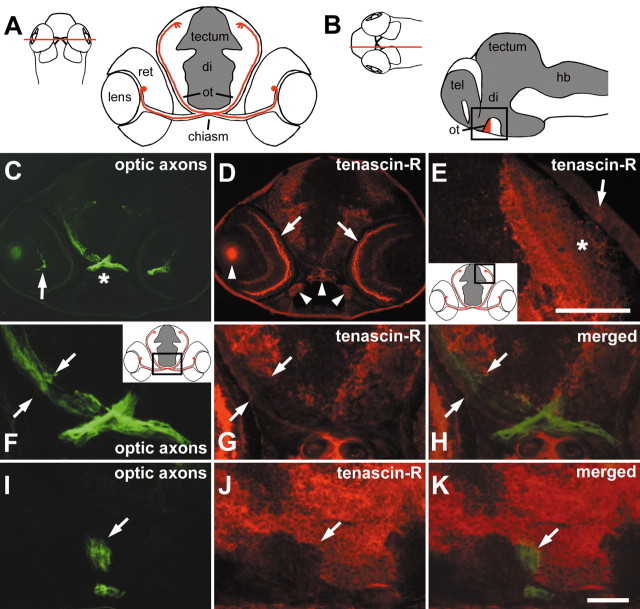
Tenascin-R immunoreactivity borders the optic projection in 3-d-old larvae. A, B, Schematic presentations of the optic projection are shown in a cross-section in A. The optic projection is represented by one retinal ganglion cell in red with its soma located in the retina (ret) and its axon entering the diencephalon (di) through the chiasm, where it crosses the midline and reaches the superficial optic neuropil of the optic tectum (tectum) through the optic tract (ot). InB, the ventral optic tract (red) is indicated in a sagittal section (tel, telencephalon; hb, hindbrain). Cell-dense areas are depicted in gray. Red lines in dorsal views of whole heads indicate approximate levels of sectioning. C, D, A cross-section through a head at the level of the optic chiasm as indicated in A, double immunolabeled for optic axons (C, green) and tenascin-R (D, red), is shown. Optic axons are labeled from the optic fiber layer of the retina (arrow in C) through the chiasm (asterisk in C) into the ventral diencephalon. Tenascin-R immunoreactivity is present in the retinal outer plexiform layer (arrows in D) and the brain. Arrowheads in D indicate nonspecific fluorescence of the lens and cartilage. E, In a cross-section through the tectum, corresponding to the boxed area in the inset, tenascin-R immunoreactivity is found primarily in deep fiber layers. The asterisk indicates the superficial optic neuropil that is low in tenascin-R immunoreactivity. The arrow indicates the epidermis overlaying the tectum. F–H, A higher magnification of the section shown in C and D corresponds to the boxed area in the inset ofF. The optic tract is indicated by opposing arrows, showing that tenascin-R (G) directly borders optic axons (F) medially. In H, signals are merged. I–K, In a double-labeled sagittal section through the brain (oriented as in the boxed area in B), the ventral optic tract is indicated by an arrow. Tenascin-R immunoreactivity (J) directly borders optic axons (I) caudally but not rostrally. In K, signals are merged. Arrows in I–K point to the ventral optic tract. Scale bars: E,50 μm; (in K) C, D, 100 μm and F–K, 33 μm.