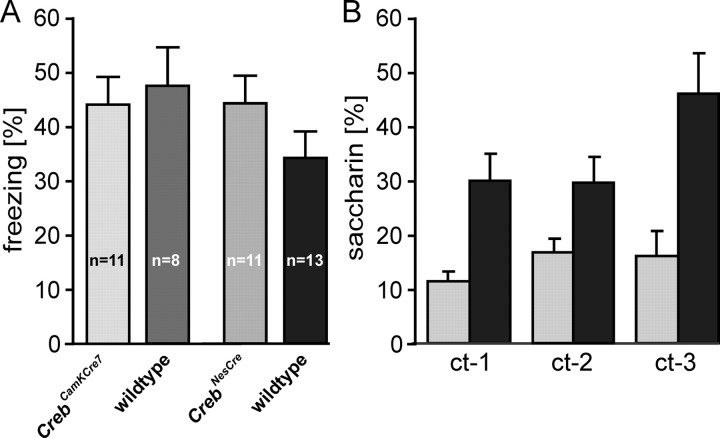
Figure 6.
Loss of CREB does not affect hippocampus-dependent learning but severely impairs associative learning that depends on the activation of extrahippocampal brain regions. A, Reduction of CREB does not result in significant changes in context-dependent fear conditioning, a task that is contingent on the functional integrity of the hippocampus. The two mutant strains show freezing scores similar to those obtained for their respective littermate groups, indicating unimpaired LTM. B, Creb mutants display a significant attenuation of conditioned taste aversion, a hippocampus-independent associative learning paradigm. CrebNesCre mice (filled bars) avoided saccharin less than wild types (p < 0.0001) during three choice tests separated by 24 hr (ct-1–ct-3). Animals of both genotypes developed the same preference for the saccharin solution when its first consumption during conditioning was followed by vehicle injection not inducing malaise (saccharin preference is indicated by the gray bar). Mean ± SEM are shown.