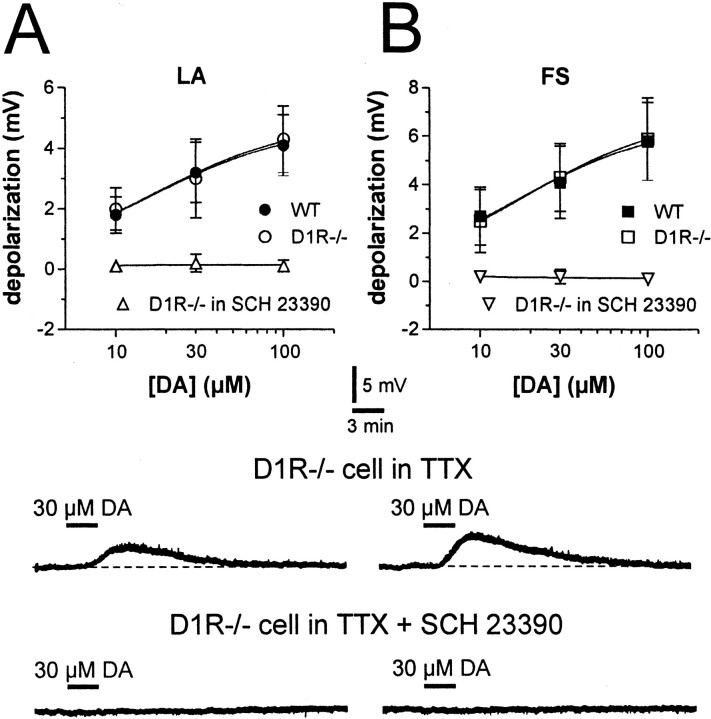
Figure 2.
Dopamine depolarizes LA and FS interneurons of both WT and D1R-/- mice. A, The graph shows the dose–response relationship for the depolarizing effect of DA on LA interneurons from WT and D1R-/- mice (in the control condition and in the presence of 10 μm SCH 23390). Electrophysiological traces from a single experiment show that bath application of 30 μm DA (black line), in the presence of 1 μm TTX, produces a reversible membrane depolarization in a D1R-/- LA interneuron (top trace). In the same cell, the depolarizing effect of DA is fully prevented by the DA D1-like receptor antagonist SCH 23390 (10 μm; bottom trace). B, The graph shows the dose–response relationship for the depolarizing effect of DA on FS interneurons from WT and D1R-/- mice (in the control condition and in the presence of 10 μm SCH 23390). Electrophysiological traces from a single experiment show that bath application of 30 μm DA (black line), in the presence of 1 μm TTX, produces a membrane depolarization in a D1R-/- FS interneuron (top trace). In the same neuron, the depolarizing effect of DA is fully prevented by the DA D1-like receptor antagonist SCH 23390 (10 μm; bottom trace). Resting membrane potentials are -58 mV in A and -78 mV in B.