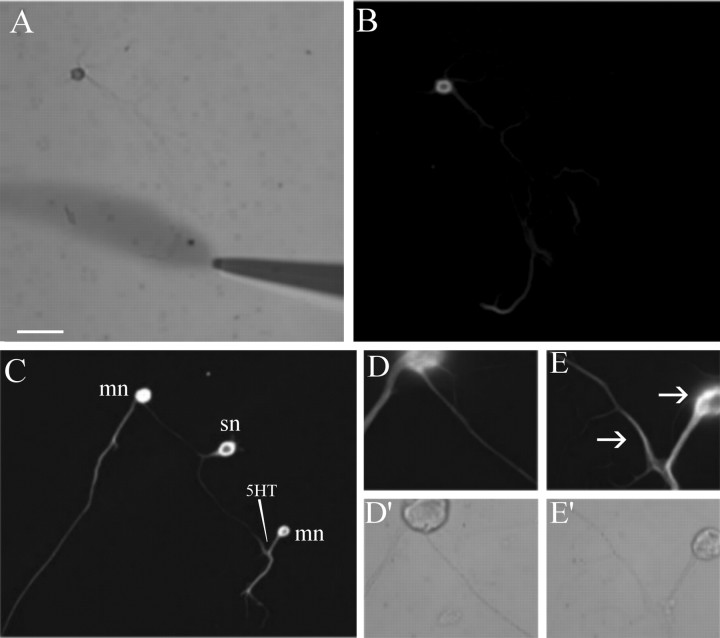
Figure 7.
Local application of 5-HT produces a local increase in α-tubulin immunoreactivity. Aplysia sensory neurons were cultured for 5 d, and five pulses of 5-HT were applied locally to a distal neurite (differential interference contrast image; A). Fifteen minutes after the last pulse of 5-HT, the cells were fixed and stained with anti-α-tubulin antibodies (B). A bifurcated Aplysia sensory neuron (sn) making contact with two spatially separated LFS motor neurons (lfs) was cultured for 5 d, and five pulses of 5-HT were applied to the connection made onto one motor neuron, such that neither the sensory cell body nor the connections made onto the other motor neuron were exposed to the 5-HT (C). Increased α-tubulin immunoreactivity was detected at the connection made onto the treated (E) motor neuron compared with the untreated (D) connection; differential interference contrast images in D′, E′). Arrows point to increased immunoreactivity in distal sensory neurite and in sensory neuron varicosity forming on LFS motor neuron cell body. Scale bar (in A): A-C, 100 μm; D, E, 40 μm.