Figure 4.
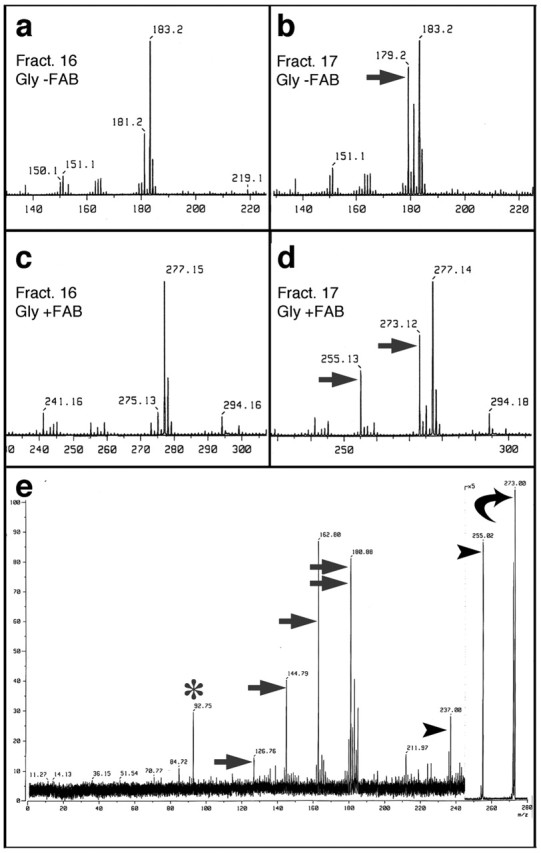
Identification of the axon-promoting factor by mass spectrometry. a, b, Fast atomic bombardment mass spectra in the negative ion mode (FAB-), m/z range of 140-220, in the presence of glycerol (gly). LC-NH2 column fraction 17, which stimulated outgrowth, contains a peak with m/z = 179.2 (b, arrow) that is not seen in the adjacent, inactive column fraction (16, a). m/z values in the negative ion mode represent the true mass minus 1 proton. c, d, FAB mass spectra in the positive ion mode (FAB+), m/z range of 230-300, in the presence of glycerol. The active fraction (17, d) contains peaks with m/z = 273.12 and 255.13 (arrows) that are absent in the adjacent inactive fraction (16, c). m/z values in the positive ion mode represent the true masses plus one proton. e, FAB+ MS/MS analysis of the m/z = 273 species from d (curved arrow). When subjected to higher voltage, the m/z 273 species generated a glycerol peak (m/z = 93; asterisk) and an ion of m/z = 181 (double arrow), i.e., the parent species minus glycerol; most of the additional ions represent successive losses of 18 atomic mass units from either the 181 ion (m/z = 163, 145 and 127; arrows) or from the glycerol adduct of the 181 species (m/z = 255, 237; arrowheads). These results indicate that the axon-promoting factor is a carbohydrate with the formula C6H12O6.
