Figure 2.
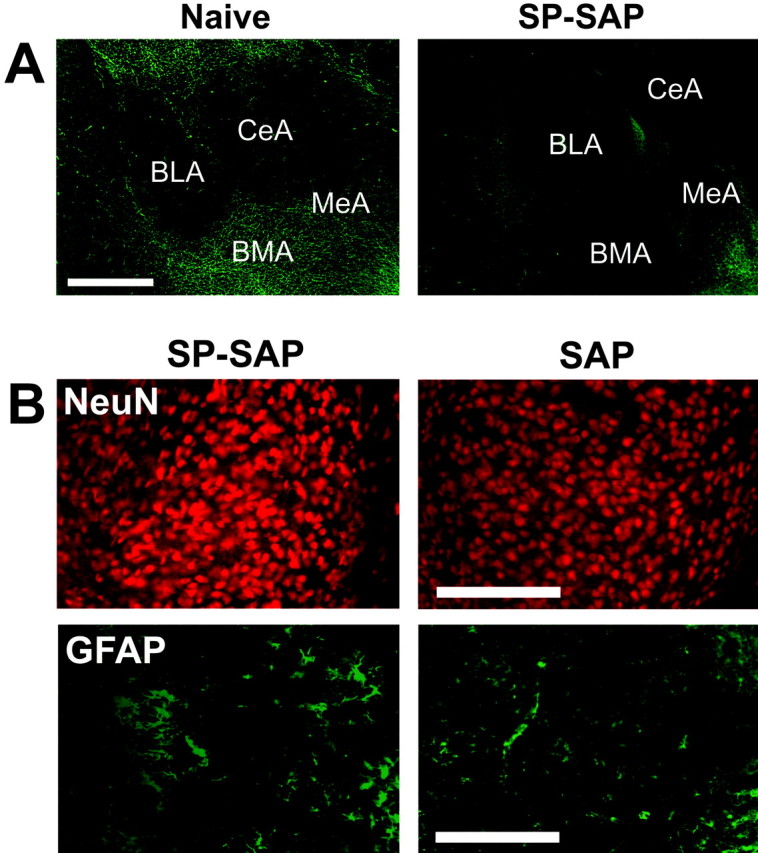
Effects of SP-SAP in the amygdala. A, Sections from the amygdala of a naive and SP-SAP-injected mouse stained immunohistochemically for the NK1 receptor. After 5 weeks, SP-SAP caused a reduction in NK1 receptor immunoreactivity around the injection site, particularly in the medial (MeA), basomedial (BMA), and central (CeA) nuclei. Scale bar, 1 mm. B, Sections from the medial nucleus stained immunohistochemically for NeuN or GFAP. Loss of NK1 receptor immunoreactivity was not accompanied by loss of NeuN immunoreactivity or increases in GFAP immunoreactivity. Injection of SAP alone also failed to bring about loss of neurons or gliosis at the injection site. Sections from naive mice and SP-injected mice (data not shown) were similar to those injected with SAP. Scale bar, 250 μm. BLA, Basolateral nucleus of the amygdala.
