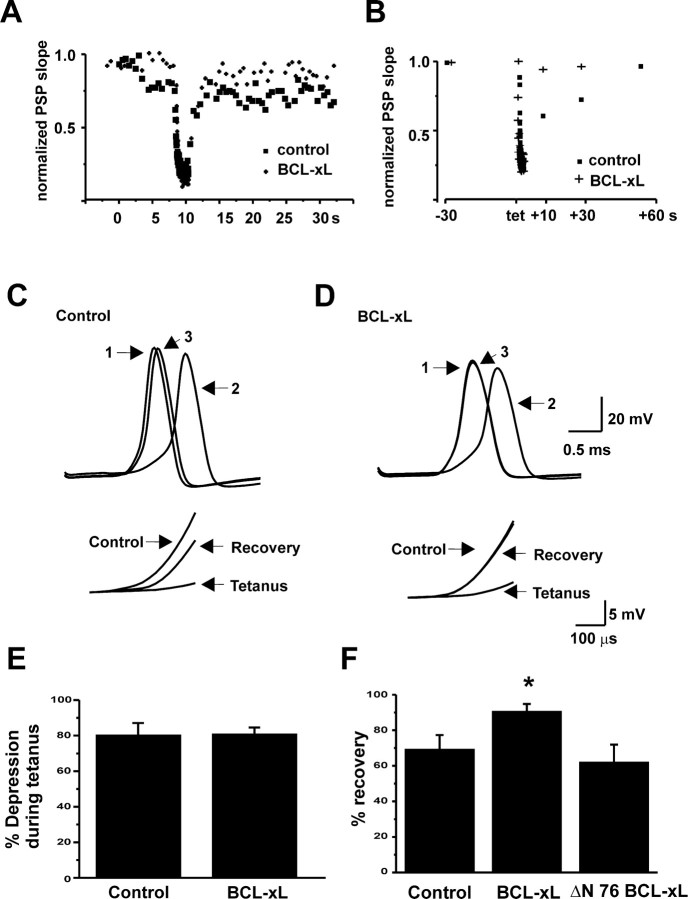
Figure 5.
Effects of BCL-xL injection on recovery from a tetanus. A, Time course of synaptic depression and recovery from depression in response to a tetanus (50 Hz, 2 sec) given during basal stimulation at 2 Hz, before and 9 min after injection of BCL-xL. B, Time course of recovery from depression in response to a tetanus given during basal stimulation at 0.033 Hz, before and after injection of BCL-xL. Postsynaptic responses were evoked at 10, 30, or 60 sec after the tetanus. C, Postsynaptic responses before (1), during (2), and 30 sec after (3) a tetanus during basal stimulation at 0.033 Hz. Data were obtained before the effect of BCL-xL. The inset shows rates of rise of postsynaptic responses on an expanded scale. D, Postsynaptic responses for the same cell recorded 50 min after injection of BCL-xL. E, Bar graphs comparing the pretetanus rate of rise of postsynaptic responses with that of the last response in the train for controls and synapses injected with BCL-xL. F, Bar graphs showing percentage recovery of postsynaptic responses 30 sec after a tetanus. BCL-xL responses were significantly increased over control (*p < 0.03). For controls, n = 10; for BCL-xL, n = 6; for ΔN 76 BCL-xL, n = 4.