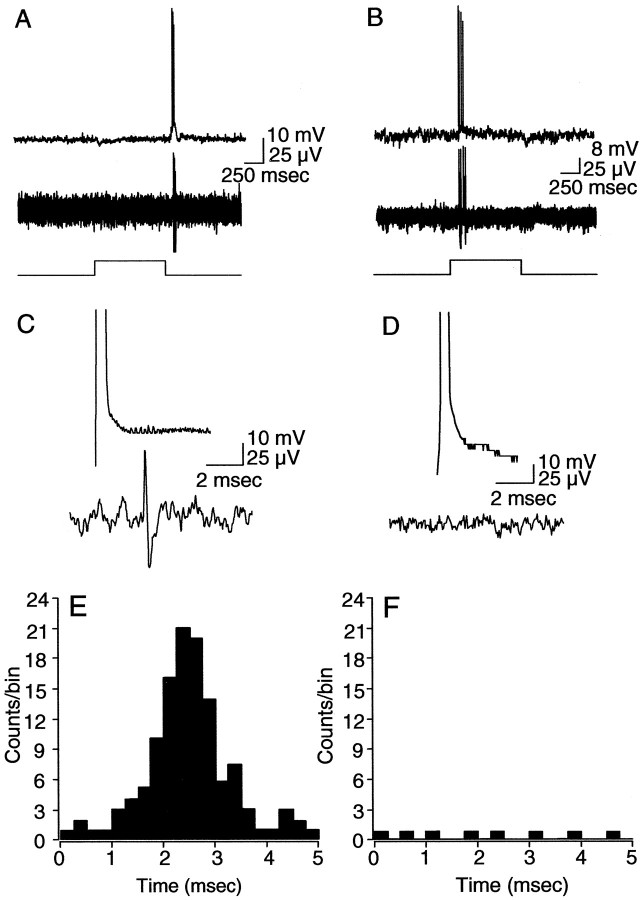
Figure 9.
Spikes generated in α-GCs with extrinsic current injection. A, B, Simultaneous intracellular and extracellular recordings from pairs of off-center (A) and on-center (B) α-GCs. Responses are to a full-field stimulus with intensity in the low scotopic range (4.7 Rh* · rod-1 · sec-1). Light traces at bottom indicate onset and offset of the light stimulus. C, D, Same pairs of cells showing anodal break spike produced in one cell after negative current injection through the intracellular microelectrode and the simultaneous extracellular recording from the neighboring cell. Anodal break spike in the off-center α-GC produced a spike in the neighboring off-center cell with a latency of ∼2.5 msec. Anodal break spike in the on-center α-GC produced no spike in the on-center α-GC neighbor. Top and bottom amplitude calibrations apply to intracellular and extracellar recordings, respectively. E, F, Cumulative histograms showing the latency between spikes generated in simultaneously recorded pairs of off-center (E) (n = 4) and on-center (F) (n = 2) α-GCs after generation of an anodal break spike in one cell of each pair. Whereas 22% (121 of 550) of anodal break spikes generated in off-center α-GCs resulted in a spike in a neighboring off-center α-GC with a latency of <5 msec, only 0.04% (8 of 200) of anodal break spikes in on-center α-GCs were paired with a spike in a neighboring α-GC. The short-latency synchronous spiking of off-center cells after current injection showed a peak latency of ∼2.4 msec.