Figure 2.
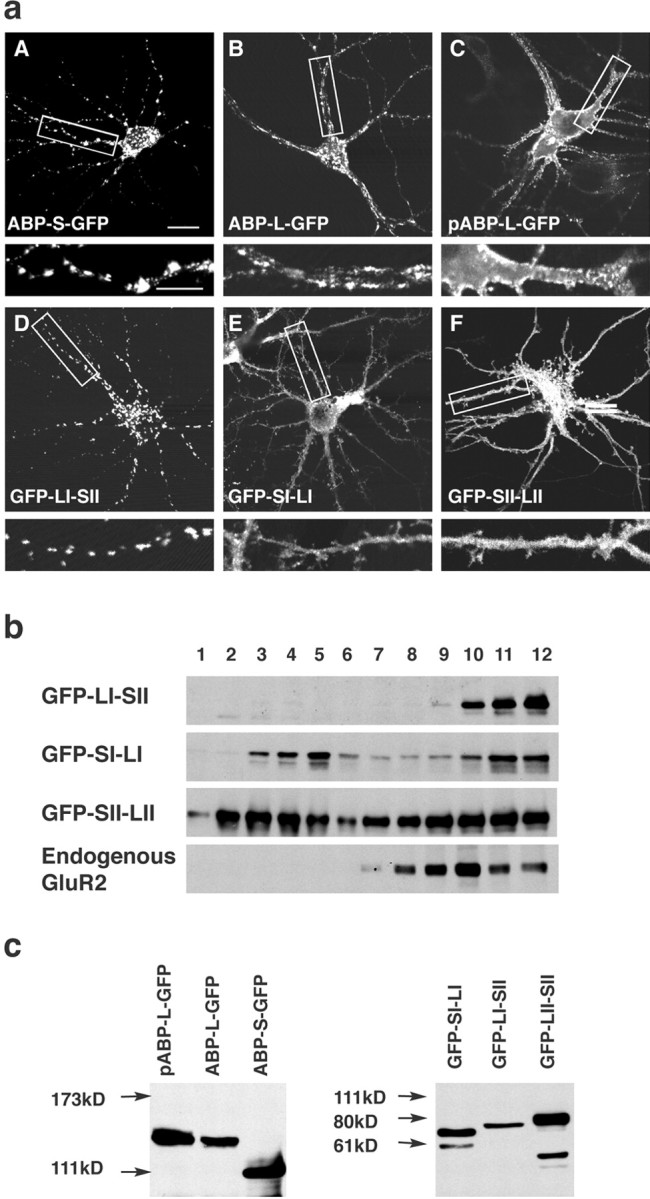
The LI-SII ABP fragment forms internal clusters in hippocampal neurons. a, Hippocampal neurons were infected with Sindbis viruses expressing different full-length isoforms of ABPs or fragments of ABP, all tagged with GFP as indicated. ABPs or fragments of ABP were detected by GFP fluorescence with confocal microscopy. ABP-S-GFP was seen in internal clusters in the cell body and dendrites (A). ABP-L-GFP was for the most part localized in clusters similar to those of ABP-S-GFP, but also distributed to a significant extent at the surface of dendrites (B). pABP-L-GFP was located at the membrane of the cell body and dendrites, as well as in spines (C), and GFP-LI-SII was found extensively in internal clusters (D), whereas GFP-SI-LI and GFP-SII-LII were directed to the cell body, dendrites, and spines (E, F). The bottom panels are enlargements of the areas indicated in the top panels. Scale bars: top panels, 20 μm; bottom panels, 10 μm. b, Sucrose gradient fractionation of lysates of cortical neurons expressing different fragments of ABP. Cortical neurons were infected with viruses that express ABP fragments. GFP-LI-SII and endogenous GluR2 sedimented rapidly, in fractions 9-12, whereas GFP-SI-LI and GFP-SII-LII were widely distributed and present in both slowly and rapidly sedimenting fractions, fractions 2-5 and 9-12, respectively. c, HEK293T cells were transfected with cDNAs encoding different forms of ABP and ABP fragments, all tagged with GFP. After 48 hr of transfection, cell lysates were separated on SDS gel, and proteins were visualized by Western blot with anti-GFP antibody. All of the expressed protein bands displayed the anticipated mobility.
