Figure 4.
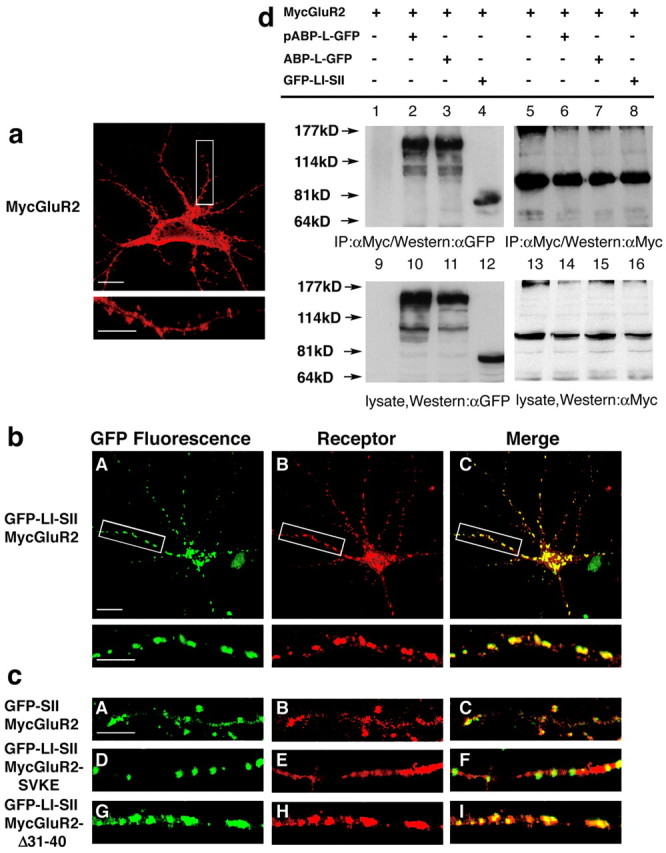
The LI-SII fragment colocalizes and clusters with MycGluR2. a, Hippocampal neurons were infected with a Sindbis virus expressing MycGluR2. After 24 hr of infection, MycGluR2 was detected with the anti-Myc antibody and was distributed diffusely in the cell body, dendrites, and spines. The bottom image is an enlargement of the boxed area in the top image. Scale bars: top image, 20 μm; bottom image, 10 μm. b, Hippocampal neurons coexpressing GFP-LI-SII with MycGluR2. GFP-LI-SII not only formed clusters of its own (A) but also induced MycGluR2 clusters (B). The merged image (C) revealed coclusters of GFP-LI-SII and MycGluR2. The bottom images are enlargements of the boxed areas in the top images. Scale bars: top image, 20 μm; bottom image, 10 μm. c, Control coinfections of hippocampal neurons. GFP-SII and MycGluR2 colocalized in dendrites and spines (A-C). GFP-LI-SII formed clusters, but it did not induce MycGluR2-SVKE clusters (D-F). GFP-LI-SII coclusters with MycGluR2-Δ31-40 (G-I). Clustering requires LI and the interaction of SII with the GluR2 C terminus, but not the NSF binding region of the GluR2 C terminus, residues 31-40. Scale bar, 10 μm. d, HEK293T cells were transfected with the cDNAs encoding MycGluR2 alone or in conjunction with pABP-L-GFP, ABP-L-GFP, and GFP-LI-SII. After 48 hr of transfection, cells lysates were immunoprecipitated with a monoclonal antibody against Myc and blotted with anti-GFP (αGFP) serum (lanes 1-4) and anti-Myc (αMyc) (lanes 5-8). Lysates were also probed with anti-GFP serum (lanes 9-12) or anti-Myc (lanes 13-16), respectively, to confirm the comparable expression levels of all of the proteins.
