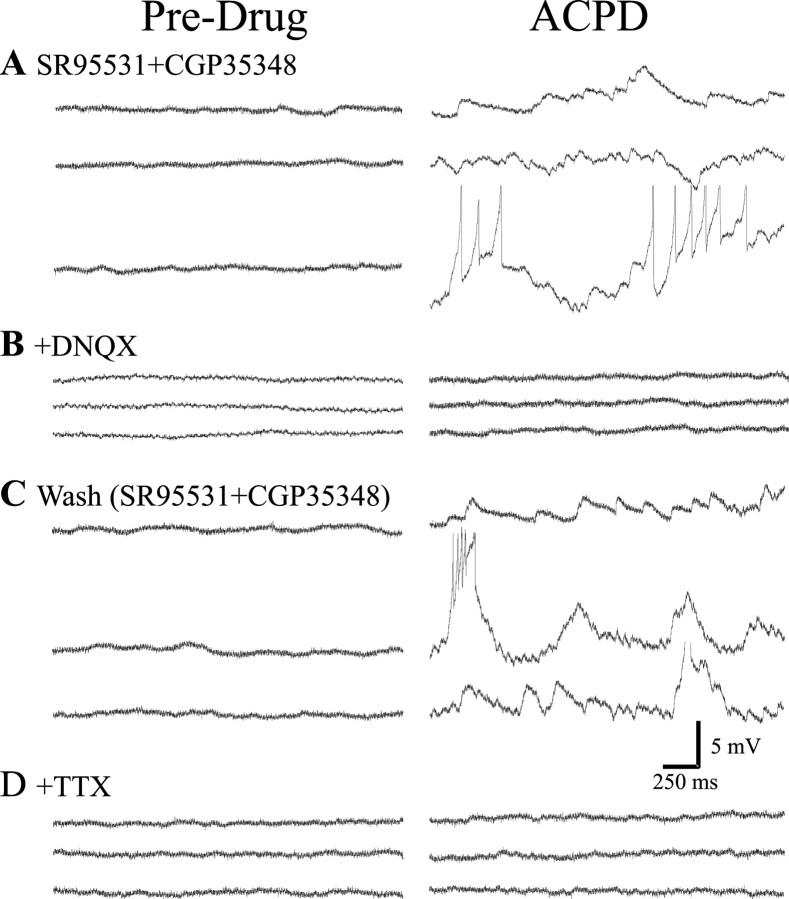
Figure 4.
ACPD increases spontaneous EPSPs in interneurons. A, In a recording from geniculate interneuron, excitatory spontaneous activity was isolated by antagonizing GABA receptors with SR-95531 (20 μm) and CGP35348 (200 μm). Under these conditions, application of ACPD (250 μm) produced a robust increase in spontaneous membrane depolarizations. This increased activity could produce spike discharge (truncated), depending on the resting membrane potential of the neuron. B, After the addition of the non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist DNQX (30 μm), ACPD produced no apparent change in baseline activity, indicating that the depolarizations were likely EPSPs. C, After washout of DNQX, the ACPD-mediated increase in spontaneous EPSPs was similar to that observed in A. D, Synaptic activity was then attenuated by TTX (1 μm), and, once again, the ACPD-mediated increase in spontaneous EPSP activity was completely attenuated.