Figure 5.
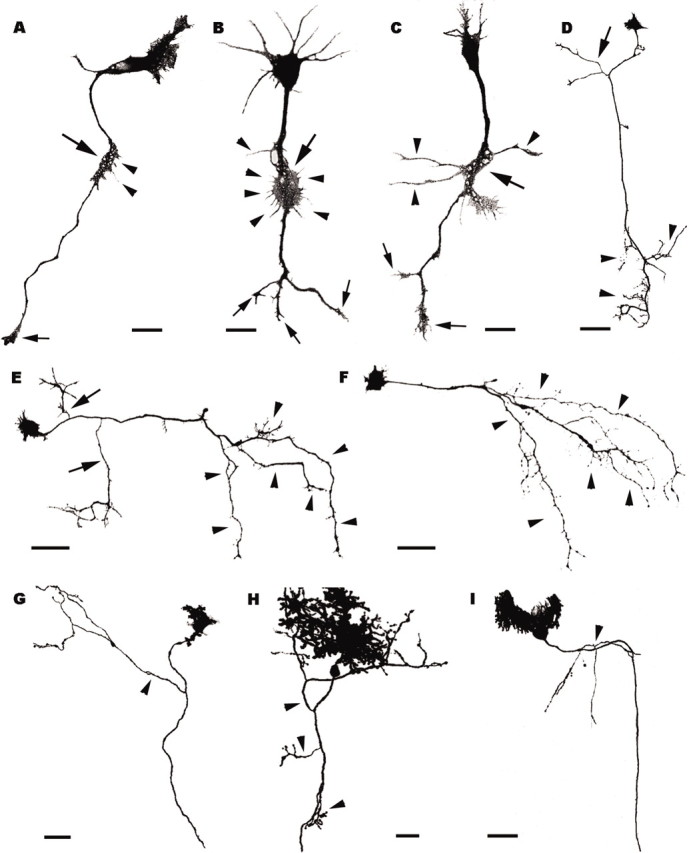
Axon branching pattern of Purkinje cells grown in vitro (A–F) or transplanted to extracerebellar CNS regions (G–I). A–C, Three Purkinje cells after 5 d in vitro; large arrows point to the lamellipodia-like swellings located along the axons, behind the leading growth cones (small arrows). Thin filopodia (A, B, arrowheads) or longer processes (C, arrowheads) sprout from such swellings. D–F, Purkinje cells after 20 d in vitro; arrowheads indicate terminal arbors, whereas arrows in D, E point to collateral branches. Note that the Purkinje cell in F has no collateral ramifications. G–I, Transplanted Purkinje cells grown in extracerebellar CNS regions (G, diencephalon; H, mesencephalon; I cerebral cortex); arrowheads point to collateral ramifications. All panels are confocal stacks of calbindin-immunofluorescent (A–F) or EGFP-expressing (G–I) Purkinje cells. Scale bars: A–C,20 μm; H,30 μm; D–G, I, 50 μm.
