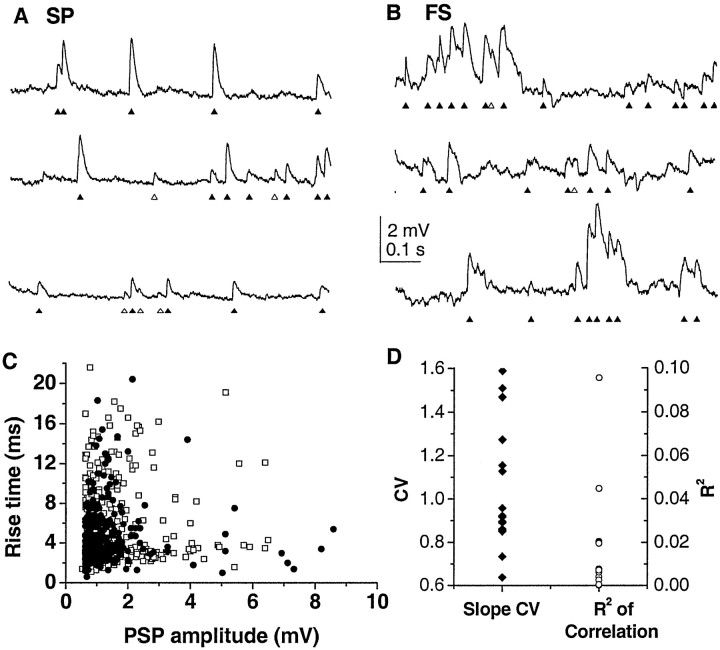
Figure 3.
Spontaneous synaptic events in striatal neurons during the down state (current clamp) in spiny projection neurons (SP; A) and fast spiking interneurons (FS; B). Traces represent contiguous segments. Activity is characterized by the presence of spontaneous events that resemble synaptic inputs at down-state potential. ▴, Identified events; ▵, putative events missed by the algorithm or misclassified. Down-state potential is -93 mV (SP) and -57 mV (FS), respectively. Note the occurrence of multiple PSPs with an IEI too short for the membrane potential to return to resting potential in the FS. C, Rise time versus amplitude is uncorrelated for both spiny projection neurons and fast spiking interneurons, suggesting a heterogeneous population of synapses. D, Summary of PSP slope characteristics for all neurons. Low R2 values indicate the absence of correlation between PSP amplitude and PSP rise time. Similarly, relatively high coefficient of variation (CV) values demonstrate large variations in PSP slope for all neurons.