Figure 5.
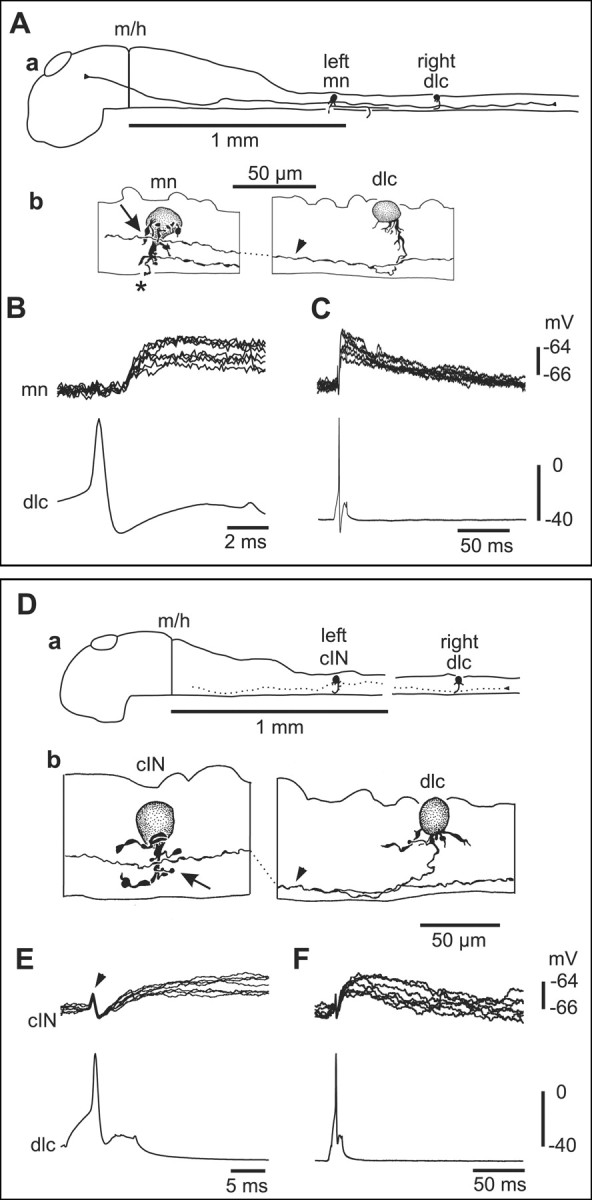
Paired recordings show that sensory pathway dlc interneurons excite a contralateral motoneuron and commissural IN at short and constant latency. A, a, Scale drawing of the CNS viewed from the left side to show the dlc interneuron, with multipolar soma at the dorsal edge of the spinal cord on the right side, has a ventral commissural axon that branches after crossing to the left side. Here, its ascending axon has possible contact sites onto a motoneuron. b, Multipolar motoneuron soma at the fourth segment on the left side with a possible contact point from the dlc axon (arrowhead) on its dendrites (arrow). The mn has a ventral descending axon and a broken peripheral axon (asterisk). B, Current injection evoking an action potential in the dlc interneuron, shown in A, leads to a small EPSP in the mn at constant and short latency (overlapped traces). C, The same record as B showing the long duration of the EPSP. D, a, Scale drawing to show a right dlc interneuron and left cIN. b, Possible synaptic contact (arrow) between the dlc axon (arrowhead) and cIN dendrite.E,F,Small slow-rise cIN EPSPs produced by dlc spikes evoked by current in jection. The artifact (arrowhead) caused by the presynaptic dlcaction potential has not been subtracted.
