Figure 1.
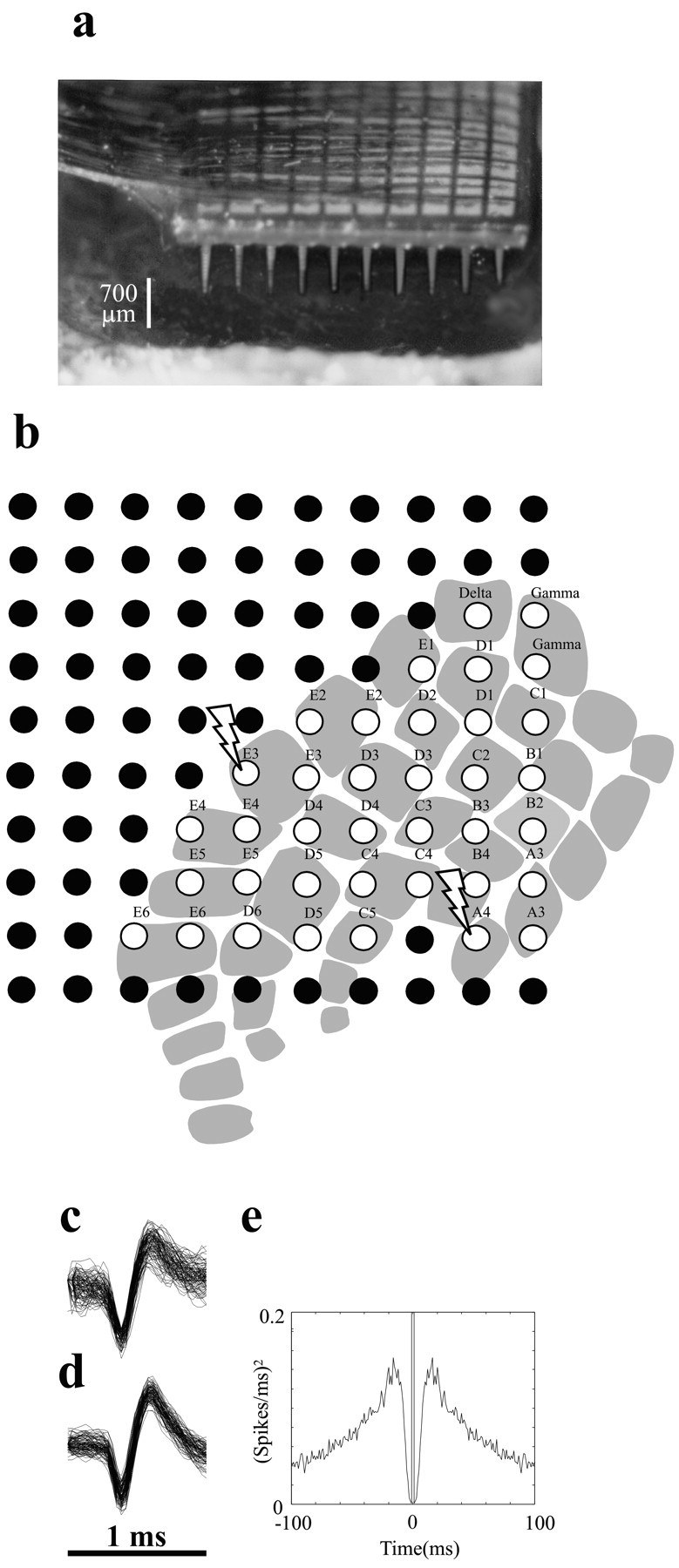
Multielectrode parallel recordings in rat barrel cortex. a, Photograph of a 10 × 10 array of microelectrodes implanted in rat somatosensory cortex in experiment 3. Interelectrode distance is 400 μm, and electrode length is 1.5 mm. Scale bar refers to the approximate 700 μm length of electrode shaft outside the brain; thus, depth of insertion was 700-800 μm. b, Placement of the microelectrode array in the barrel subfield in the same experiment. White-filled circles show the 37 electrodes at which neuronal data were recorded during whisker stimulation. The position of the array relative to the barrel columns was based on identification of the principal whisker input at each electrode of interest (see Materials and Methods). Each barrel column is designated by its row (A-E) and its arc (1-6) (Woolsey and Van der Loos, 1970). Lightning bolts designate electrodes 19 and 45, where the signals shown in c-e were recorded. c, One hundred overlaid action potential waveforms of the neuronal cluster at electrode 19. Further spike sorting was not feasible for this electrode. d, One hundred overlaid action potential waveforms of a putative unit selected from the neuronal cluster at electrode 45. e, Autocorrelogram for the putative single unit shown in d. The plot was constructed with 1 msec time bins from 2000 sec of data including spontaneous and stimulus-induced activity. The absence of spikes within 2 msec of the central bin, not observed for multi-neuron clusters, reflects the absolute refractory period of the isolated single unit.
