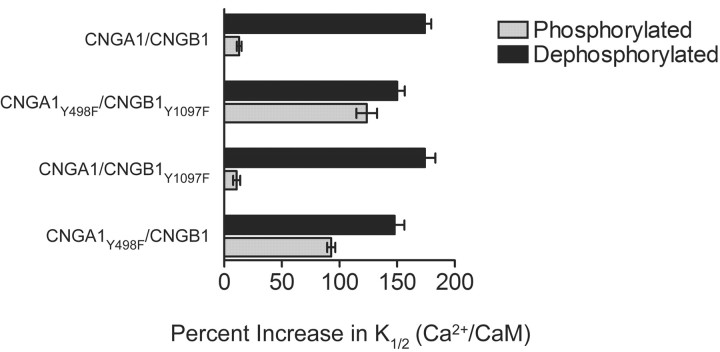
Figure 4.
Phosphorylation of CNGA1 but not CNGB1 prevents inhibition of rod CNG channels by Ca2+/CaM. The percentage increase in cGMP K1/2 values by Ca2+/CaM was calculated for each channel type based on the results in Table 1. Ca2+/CaM had little effect on channels containing wild-type CNGA1 subunits (CNGA1/CNGB1 and CNGA1/CNGB1Y1097F) when conditions promoted phosphorylation but greatly increased the K1/2 for cGMP activation when conditions promoted dephosphorylation. In contrast, Ca2+/CaM had similar effects on channels containing CNGA1Y498F channels (CNGA1Y498F/CNGB1 and CNGA1Y498F/CNGB1Y1097F) when either phosphorylation or dephosphorylation were promoted. Note that there was little difference in the phosphorylation versus dephosphorylation dependence of Ca2+/CaM modulation in channels in which the CNGB1 subunit contains the only phosphorylation site (CNGA1Y498F/CNGB1).