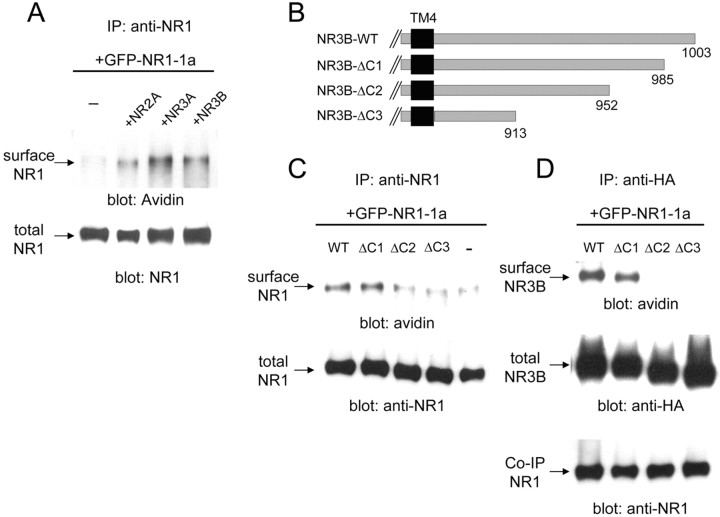
Figure 6.
Interaction of the C-terminal region of NR3B with NR1-1a is responsible for cell surface trafficking of the NMDA receptor complex. A, Cell surface biotinylation assay of cells expressing various NMDA receptors. GFP-tagged NR1-1a was coexpressed with NR2A, NR3A, or NR3B in HEK293 cells. After the cell surface biotinylation, NR1 protein was precipitated from cell lysates by an anti-NR1 antibody and subjected to immunoblot analysis using HRP-conjugated avidin (top panel). The quantity of precipitated NR1 was confirmed by immunoblotting with an anti-NR1 antibody (bottom panel). B, Deletion mutants of NR3B. Residues distal to 986 (NR3B-ΔC1), 953 (NR3B-ΔC2), or 914 (NR3B-ΔC3) were deleted (for sequences of these regions in NR3B and NR3A, see supplementary figure). C, Effects of NR3B deletion mutants on the cell surface expression of NR1. NR1-1 and the indicated HA-tagged NR3B deletion mutants were coexpressed in HEK293 cells, and cell surface biotinylation was performed. Proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) from cell lysates by an anti-NR1 antibody and subjected to immunoblotting using HRP-conjugated avidin. The quantity of precipitated NR1-1a was confirmed by immunoblotting with an anti-NR1 antibody. D, Cell surface expression of NR3B mutants coexpressed with NR1. NR1-1 and the indicated HA-tagged NR3B deletion mutants were coexpressed in HEK293 cells, and cell surface biotinylation was performed. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody and subjected to immunoblotting analysis using HRP-conjugated avidin (top panel), anti-HA antibody (middle panel), and anti-NR1 antibody (bottom panel). Results shown in A, C, and D represent those of three or four experiments. WT, Wild type.