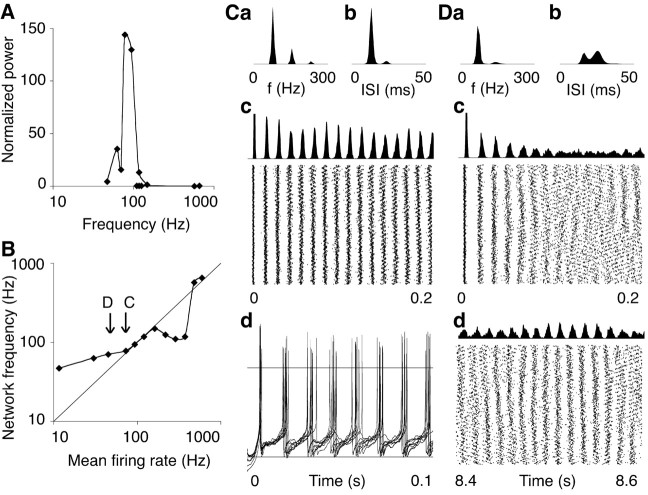
Figure 5.
Resonance in a two-dimensional network. A, Tuning curve of a triagonal network of 900 neurons, with mean weighted delay d = 3.2 msec (decay time constant τ = 3 msec). B, Frequency range of the emerging network oscillations. Over the various levels of excitation, the mean neuronal firing rate varied from 12 to 598 spikes/sec (x-axis). The resulting network oscillations were clustered on the frequency axis (y-axis) around the resonance frequency (fR = 83 Hz; range, 47-149 Hz), except at the two strongest levels of excitation, at which power was almost zero. The arrows labeled C and D indicate the levels of network excitation illustrated further in plots C and D, respectively. C, Description of the firing pattern at approximately the resonant level of excitation (mean firing rate, 73.4 spikes/sec). a, Periodogram of network activity over a simulation run of 8 sec duration. b, Mean ISI histogram averaged over all 900 neurons. c, Time histogram of population spike counts (bin width, 0.5 msec; first peak truncated at 200 spikes) and raster plot of the individual spikes fired during the first 200 msec of the simulation (CI = 0.287). d, Membrane potential traces of nine randomly selected neurons (the neurons with array indices 100, 200,... 900). Horizontal lines indicate the zero and -60 mV levels. Unequal spike heights are a graphical sampling artifact. D, Description of the firing pattern at the next lower level of excitation (mean firing rate, 45.0 spikes/sec). a, Periodogram, multiplied by a factor of 10, over a simulation run of 12 sec duration. b, Mean ISI histogram. c, Time histogram of population spike counts and raster plot of the individual spikes fired during the first 200 msec of the simulation (CI = 0.142). d, Population spike count histogram and raster plot of the individual spikes fired between 8.2 and 8.4 sec after the start of the simulation (CI = 0.092 or 0.147 after correction for the mismatch between firing rate and network frequency; Tiesinga and José, 2000).