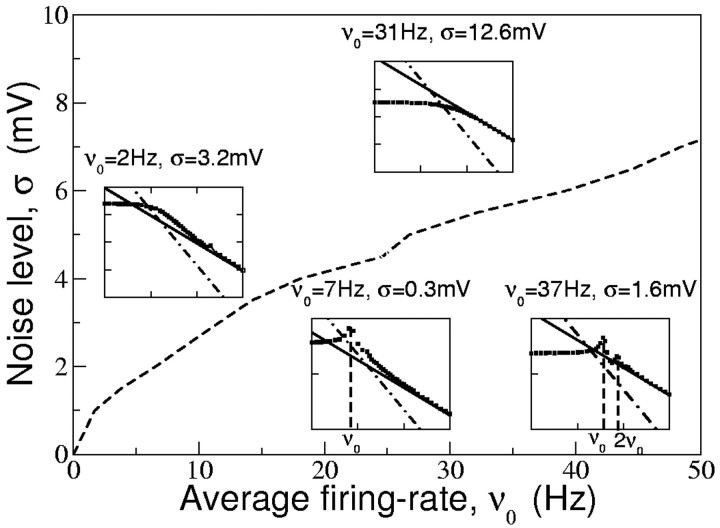
Figure 4.
The qualitative behaviors of the firing rate modulation of the EIF model at intermediate frequencies depend on the characteristics of the input current. Insets show a representative example of the corresponding behavior (gain vs input frequency in log-log scale). In all insets, we plot a simulation of the EIF model (squares, gain) and the EIF and QIF high input frequency regimes (solid and dotted-dashed lines). The dashed line gives the noise level below which there are resonant peaks at the average firing rate ν0 and possibly at integer multiples of ν0 in response. Above the dashed line, the EIF model behaves like a low-pass filter, with approximately constant gain at low frequencies and a 1/f attenuation for sufficiently high frequencies. The gain reaches the asymptotic behavior from above at low firing rates, whereas it reaches the asymptotic behavior from below for high firing rates and high noise (see differences in the two insets in the high noise region).