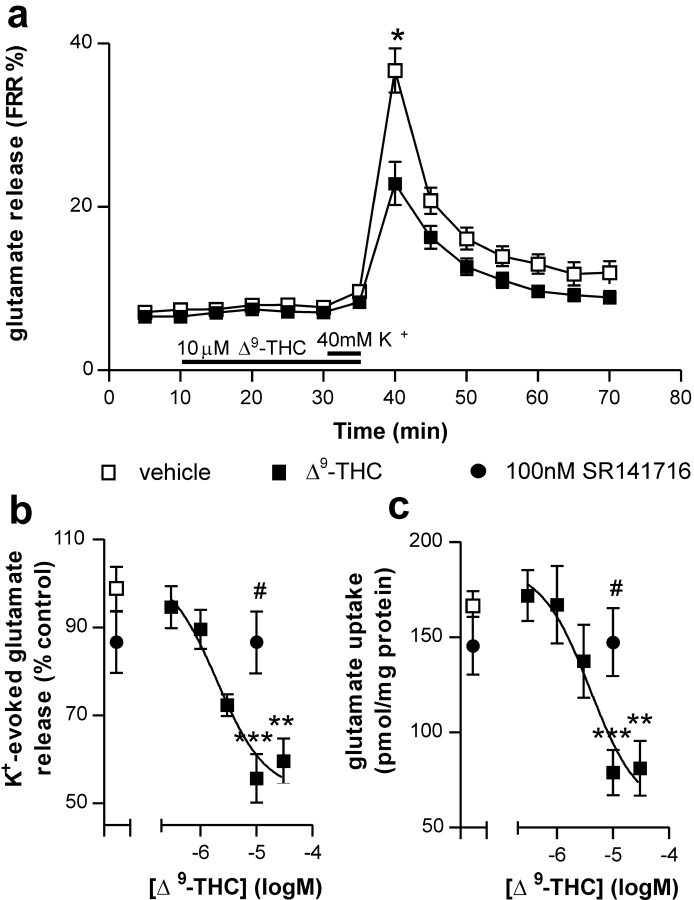
Figure 1.
Effects of THC on [3H]glutamate release and uptake in rat striatal tissue. Application of 10 μm THC reduced K+-evoked glutamate release but did not effect basal efflux (a). The effects of THC on K+-evoked glutamate release were dose dependent and were blocked by the CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716 (b). THC also dose dependently reduced glutamate uptake in an SR141716-sensitive manner (c). Data points represent averages of six (a) and 6-10 (b, c) separate experiments performed in triplicate. Filled bars in a represent timing and duration of drug addition. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. **p < 0.01 and ***p <0.001 compared with vehicle; #p < 0.05 compared with THC alone.