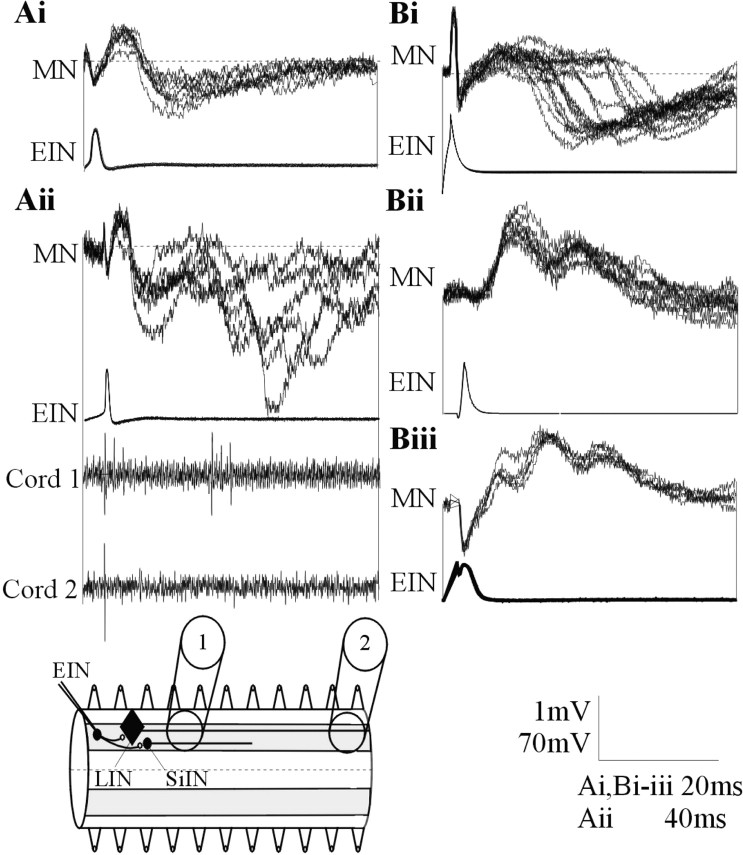
Figure 2.
Ai, In addition to the activity-dependent feedforward IPSP during spike trains, in a smaller proportion of connections, a delayed IPSP could consistently follow low-frequency (0.1 Hz)-evoked EPSPs. Aii, A single low-frequency-evoked EPSP could also be followed by several polysynaptic IPSPs. The delayed inhibitory input in this cell was associated with extracellular activity recorded in a suction electrode placed three to four segments caudal to the stimulated EIN but not in a suction electrode placed 10 segments caudal to the EIN. The diagram shows the extracellular recording arrangement and the axonal projections of the LINs and SiINs. The absence of activity in an electrode placed 10 segments caudal to the stimulated EIN suggests against LIN activation. Bi, A delayed IPSP could also develop in the absence of a direct EPSP. EIN stimulation could also result in delayed biphasic (Bii) or triphasic (Biii) excitatory inputs. MN, Motor neuron.