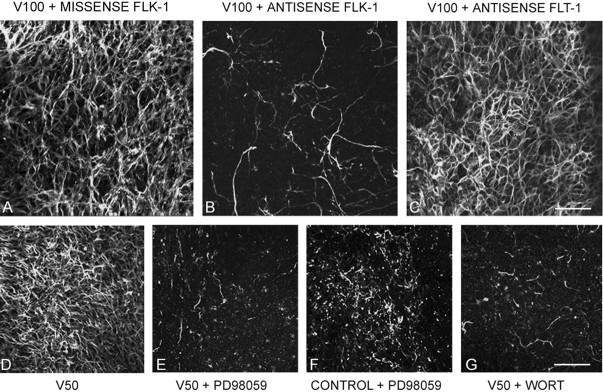
Figure 4.
Receptor mediation and signaling pathways involved in VEGF-induced neuritic growth. A, Application of 100 ng/ml VEGF and a missense ODN sequence to flk-1 shows no change in VEGF-induced TUJ1+ neuritic growth. B, Application of 100 ng/ml VEGF and AS-ODN sequence to flk-1 shows a substantial decrease in TUJ1+ processes, reminiscent of an untreated explant. C, Application of 100 ng/ml VEGF and AS-ODN to the VEGF flt-1 receptor had no effects on neuritic growth. D, Application of 50 ng/ml VEGF to cortical explant shows strong MAP-2+ immunofluorescence. E, Addition of PD98059, a MAPK (MEK) signaling pathway inhibitor, nearly eliminates neuritic growth in a sister culture to D. F, When PD98059 was added to control explants there was little qualitative difference between these and explants that also received 50 ng/ml VEGF (E), ruling out the possibility that the inhibitor indiscriminately destroyed existing neurites. G, Addition of the P13-Akt signaling pathway inhibitor wortmannin to explants that also received 50 ng/ml VEGF nearly eliminated neuritic outgrowth seen with VEGF alone. Application of wortmannin to untreated cultures had no discernable effect (not illustrated). Scale bars: (in C) A-C, 100 μm; (in G) D-G, 125 μm.