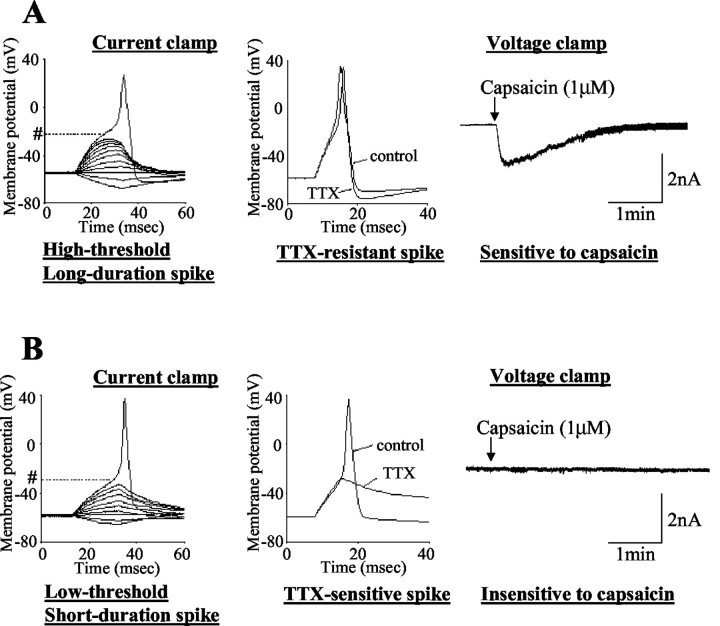
Figure 3.
Characteristics of proximal urethral afferent neurons exhibiting TTX-resistant action potentials (24μm diameter; A) and TTX-sensitive action potentials (33μm diameter; B). The left panels are voltage responses and action potentials evoked by 30 msec depolarizing current pulses injected through the patch pipette under current-clamp conditions. A pound sign followed by a dotted line indicates the thresholds for spike activation (−20 mV in A and −29 mV in B). The middle panels show the effects of TTX application (1 μm) on action potentials. The right panels show the responses to extracellular application of capsaicin (1 μm) under voltage-clamp conditions. Note that the TTX-resistant urethral afferent neuron (A) exhibited an inward current in response to capsaicin, whereas the TTX-sensitive afferent neuron showed no response to capsaicin.