Figure 6.
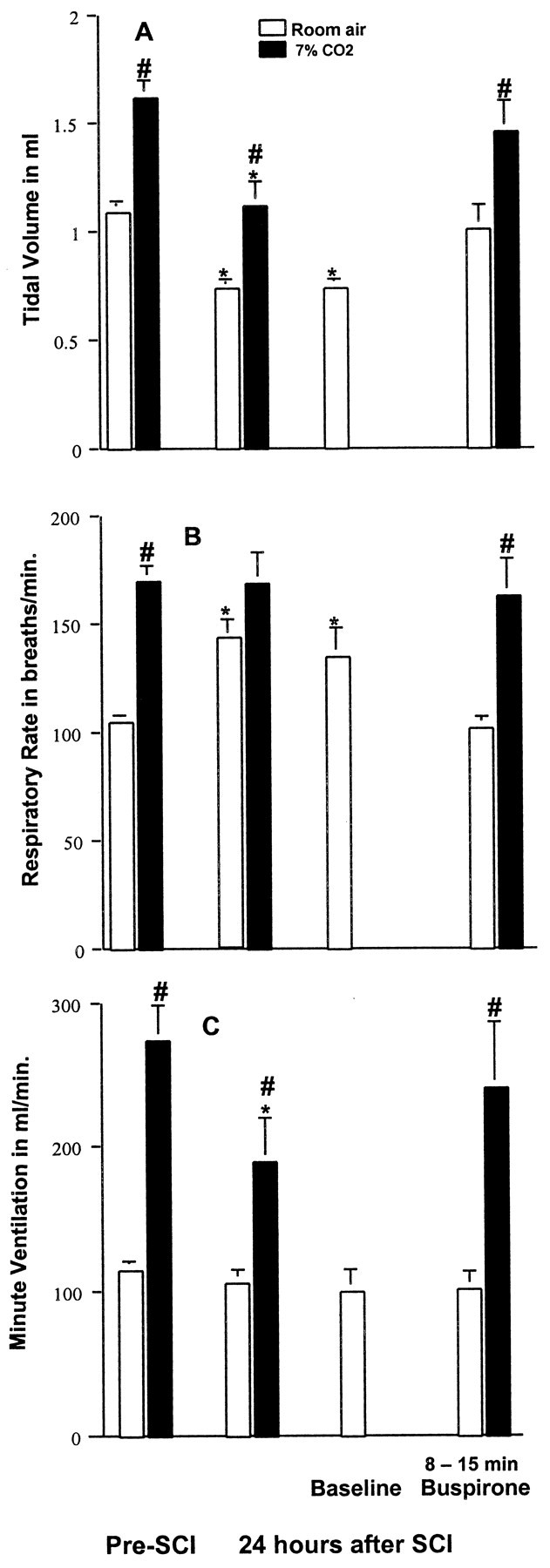
Effects of buspirone on SCI-induced respiratory dysfunction. At 24 hr after SCI, rats demonstrated reduced Vt (A) and increased f (B) with room air breathing conditions, although Ve (C) was similar to that obtained before injury. Stimulation with 7% CO2 increased Ve to a lesser extent than before injury. A baseline was re-established, and then buspirone (1.5 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered. Buspirone normalized Vt and f with room air breathing conditions and increased the response of Ve to 7%CO2 to equal that seen before SCI. Data reported are mean ± SEM for three rats and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's and Dunn's tests. *Significant difference from preinjury value obtained with the same breathing condition (room air or 7% CO2); #significant difference compared with values obtained breathing room air.
