Figure 2.
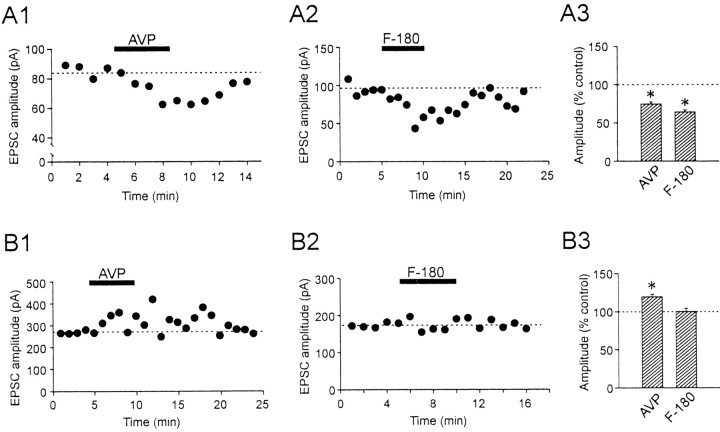
AVP differentially modulates the amplitude of the evoked EPSCs in the two types of magnocellular neurons. A1, Time-dependent plot of pharmacologically isolated EPSCs recorded from a typical AVP neuron. Each closed circle represents an average of 3-6 consecutive EPSCs elicited per minute. Bath application of AVP (2 μm) reversibly reduces the amplitude of the EPSCs. A2, The inhibitory effect of AVP was mimicked by the V1a receptor agonist F-180. A3, Summary of the effect of AVP and F-180 on EPSCs recorded from AVP neurons. B1, Time-dependent plot of evoked EPSCs in a representative OXT neuron. Bath application of AVP (2 μm) reversibly enhances the amplitude of the EPSCs. B2, In contrast to AVP neurons, F-180 has no effect on evoked EPSCs recorded in OXT neurons. B3, Summary of the effect of AVP and F-180 on EPSCs recorded from OXT neurons. *p < 0.05.