Figure 3.
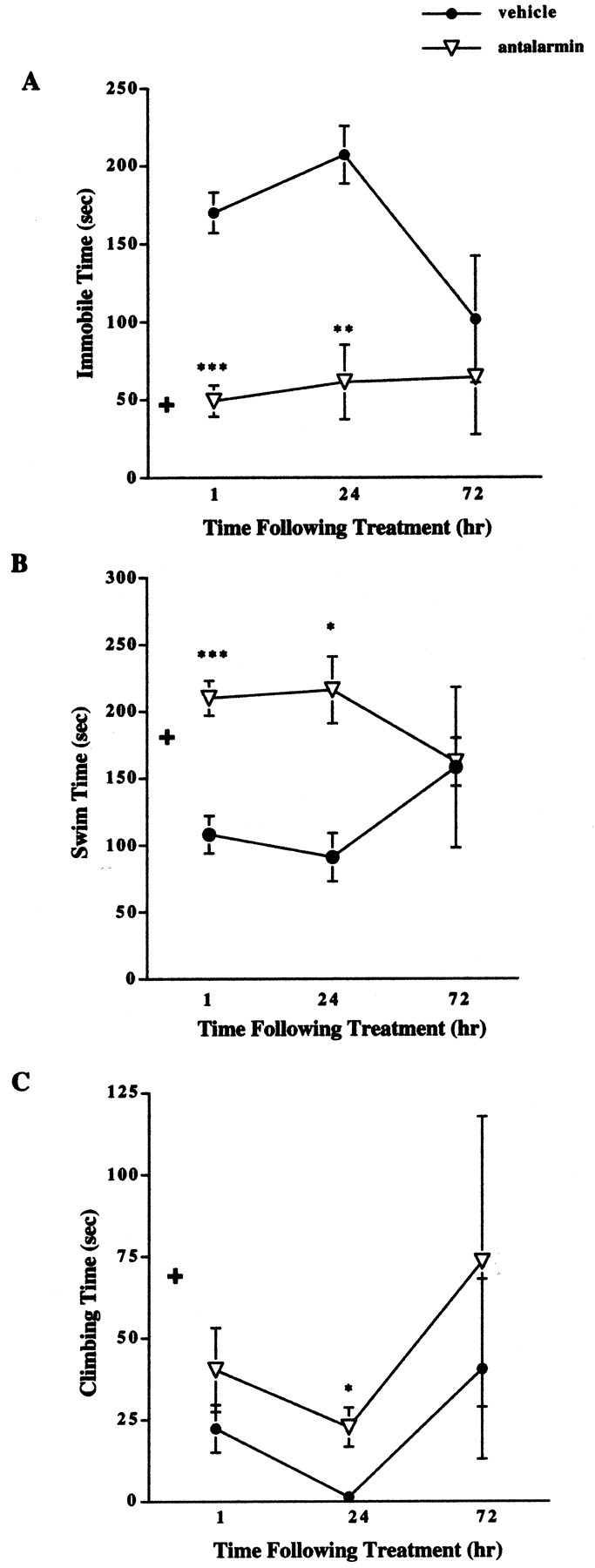
Forced swim test results after pretreatment with antalarmin in male CRFR2-deficient mice. A, Male mutant mice treated with antalarmin (7.5 mg/kg) 1 hr before testing showed decreased immobile time compared with vehicle-treated mutant mice (n = 10). ***p < 0.001. This effect remained evident 24 hr (n = 5) after treatment. **p < 0.01. No difference in immobile time was detected 72 hr (n = 5) after treatment; ANOVA and Fisher's post hoc test. + indicates basal wild-type male immobile levels for comparison.B, Male mutant mice treated with antalarmin 1 hr before testing showed increased swim time compared with vehicle-treated mutant mice (n = 10). ***p < 0.001. This effect remained evident 24 hr (n = 5) after treatment. *p < 0.05. No difference in swim time was detected 72 hr (n = 5) after treatment; ANOVA and Fisher's post hoc test. + indicates basal wild-type male swim levels for comparison. C, Male mutant mice treated with antalarmin showed increased climbing time 24 hr (n = 5) after treatment compared with vehicle-treated males. *p < 0.05. No difference was detected between antalarmin and vehicle-treated males in climbing time 1 hr (n = 10) or 72 hr (n = 5) after treatment; ANOVA and Fisher's post hoc test. + indicates basal wild-type male climbing levels for comparison.
