Figure 9.
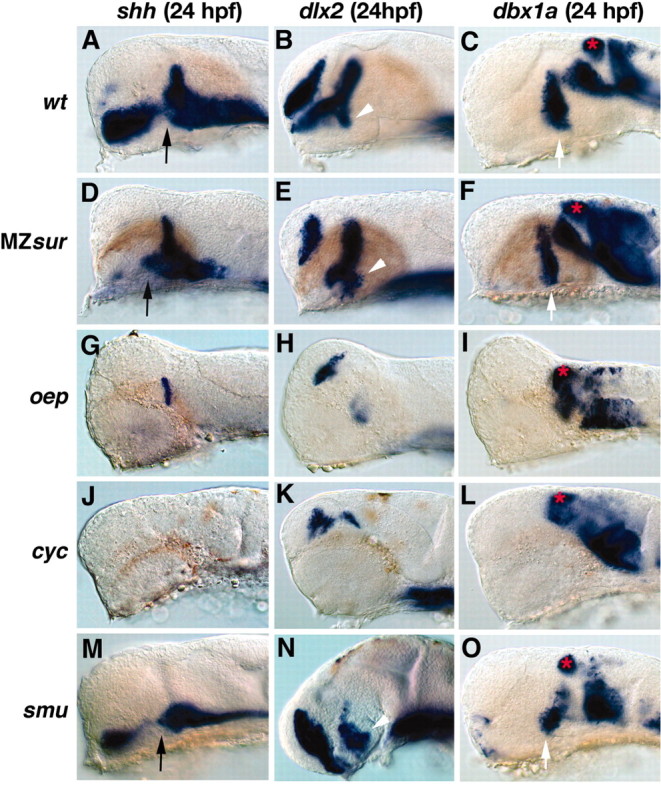
Embryonic patterning defects in the diencephalon of Nodal pathway and smu mutants. A–O, Embryos at 24 hpf (lateral views; anterior is to the left, dorsal is to the top). A–C, Wild-type embryos showing the expression domains of shh (A), dlx2 (B), and dbx1a (C). D–F, In MZsur embryos, shh expression is maintained in the zona limitans, part of the hypothalamus and midline (D), the expression domain of dlx2 in the hypothalamus is reduced in size (E); and the dbx1a expression domains in the pretectum and ventral diencephalon are present (F). G–I, oep mutant embryos show no hypothalamic expression of shh (G), dlx2 (H), and dbx1a (I), whereas the pretectal dbx1a domain is present. J–L, In cyc mutant embryos, expression of shh (J), the ventral expression domains of dlx2 (K), and dbx1a (L) in the forebrain are absent, whereas dbx1a expression in the pretectum is present. M–O, In smu mutant embryos, the expression of shh (M) in the zona limitans is absent, but a reduced expression in the ventral brain remains. The hypothalamic expression domains of dlx2 (N) and dbx1a (O), as well as the pretectal dbx1a domain can still be detected. The black arrows indicate the expression domain of shh in the ventral diencephalons. White arrowheads point to the dlx2 domain and white arrows point to the dbx1a domain in the ventral diencephalons. The red stars indicate the expression domain of dbx1a in the pretectum.
