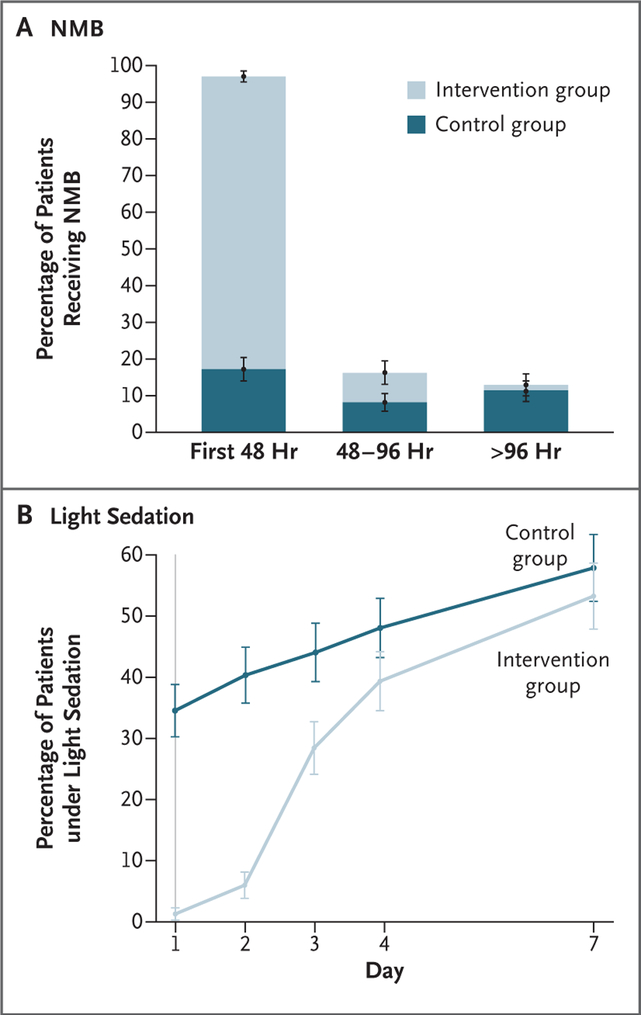
Figure 2. Neuromuscular Blockade and Sedation.
Panel A shows the mean percentage of patients who received continuous neuromuscular blockade, and Panel B shows the mean percentage of patients who were under light sedation during the first week of the trial. Light sedation was defined by a score of 0 or −1 on the Richmond Agitation–Sedation Scale (scores range from 4 [combative] to −5 [unresponsive], with a score of 0 indicating that the patient is alert and calm), a score of 3 or 4 on the Riker Sedation–Agitation Scale (scores range from 1 [unresponsive] to 7 [dangerous agitation], with a score of 4 indicating that the patient is calm and cooperative), or a score of 2 or 3 on the Ramsay Sedation Scale (scores range from 1 [anxious, restless] to 6 [unresponsive], with a score of 2 indicating that the patient is cooperative and oriented).21–23 More details are provided in Tables S3 and S4 in the Supplementary Appendix. I bars indicate standard errors.