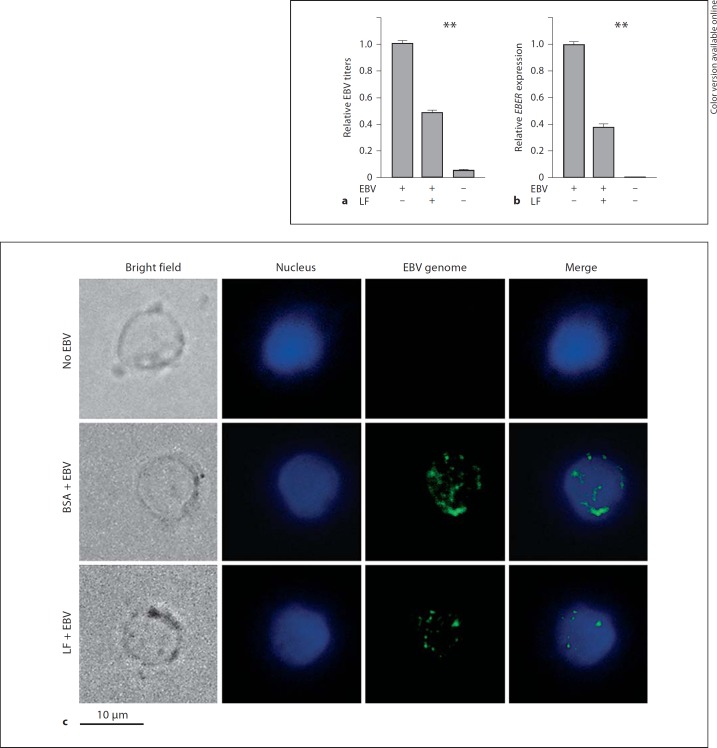
Fig. 2.
LF inhibits EBV entry. Primary B cells were incubated with hLF (50 µg/ml) or BSA (50 µg/ml) as control at 4°C for 1 h and hLF was washed away. After that, the cells were infected with EBV (MOI 50) at 4°C for 3 h and were then washed with PBS to remove unbound virus. a Total cellular and bound viral DNA was extracted, and the EBV copy number per cell (i.e. EBV titers) was determined using the Q-PCR assay of the EBV BamHI-W fragment. The EBV titer of the control treatment group (first lane) was adjusted as 1. b Total cellular RNA of the treated primary B cells was extracted, and mRNA expression levels of EBV gene EBER were measured by Q-PCR assay. The expression level of the control group was adjusted as 1. Two-way ANOVA was used to evaluate differences between the three groups. ** p < 0.01. c Detection of EBV genomes by FISH. Primary B cells were treated as above and then fixed; intracellular viral genomes were detected by green fluorescence, and nuclei were identified by DAPI staining.