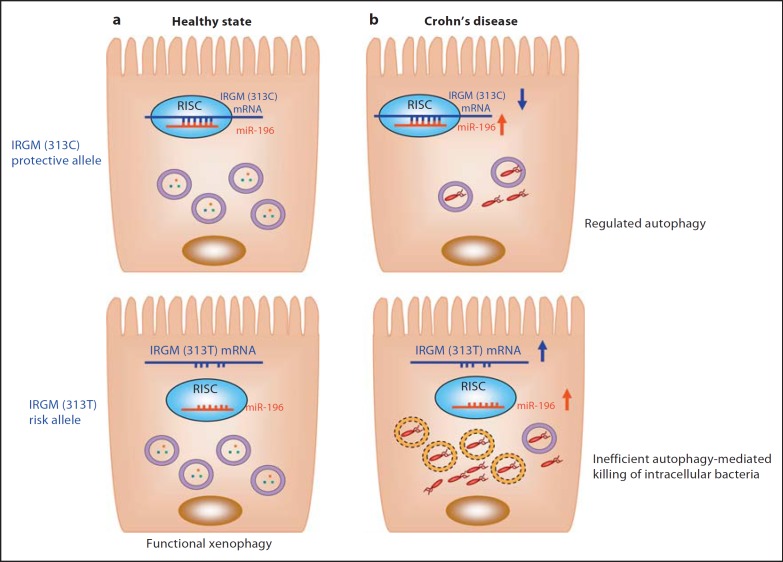
Fig. 3.
Hypothetical model for the involvement of the CD-associated IRGM (c.313C>T) in autophagy, bacterial clearance and CD. a MicroRNA 196 (miR-196) normally targets IRGM mRNA within RISC for a negative regulation. The IRGM (c.313C>T)risk allele mRNA, however, lacks the binding site for miR-196 and therefore is not regulated by this microRNA. The IRGM risk variant does not cause alterations in autophagy during healthy states. b During CD, expression of miR-196 is increased, which leads to a downregulation of IRGM expression. This results in a decrease in autophagic flux accompanied by a decrease in autophagosome-associated intracellular bacteria (upper panel). In subjects with the IRGM risk variant (bottom panel), IRGM expression is not inhibited by miR-196 and is upregulated, leading to defective xenophagy with a decrease in the percentage of intracellular bacteria captured in functional acidic vacuoles (violet circle) in comparison with that in IRGM (c.313C) protective variant-bearing subjects. Most intracellular bacteria replication occurs in nonmature vacuoles (yellow dotted circle). This consequently results in intracellular bacteria overload, which could further worsen disease status.