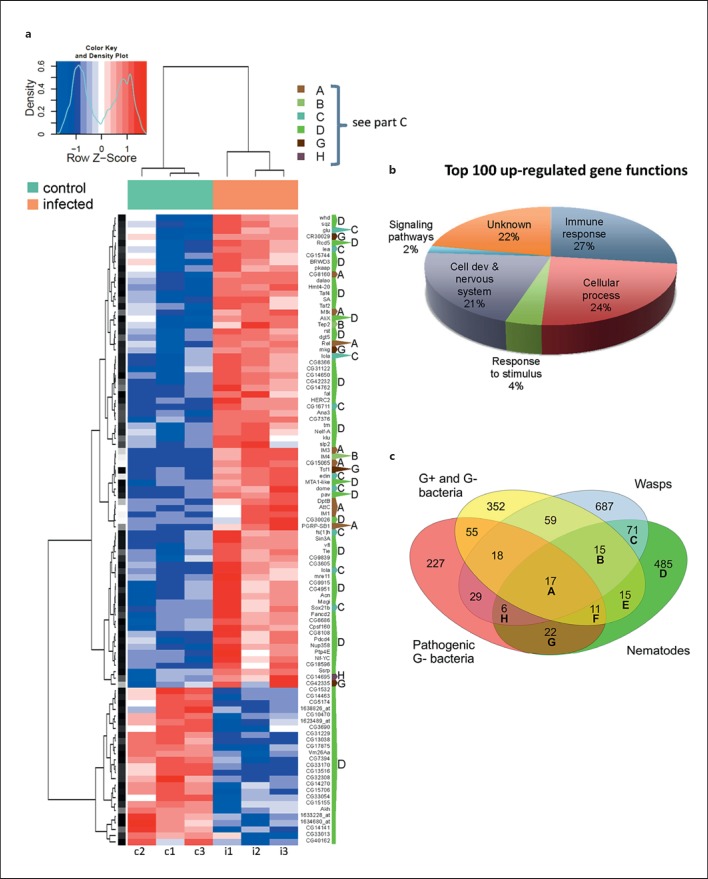
Fig. 2.
The significantly regulated transcripts after nematobacterial infection are enriched for immune genes. a A heatmap representing the 100 most strongly regulated transcripts from the microarray (columns c1-c3 = Control: noninfected; i1-i3 = infected larvae). Each column represents an independent sample. Color key and density plot represent the level of regulation. Dark intensities indicate the most up- and down-regulated genes, respectively. The one-letter code to the right of the heatmap indicates whether the gene was previously detected in other genome-wide analysis of Drosophila larval immune response (category A-C, G, H) or is specifically regulated upon nematode infection (D); for a description of the categories compare the Venn diagram in c. b GO classification of the 100 most strongly up-regulated genes. Immune response molecules occupy a fourth of the top 100 genes (see also online suppl. table 2). c Venn diagram showing differentially regulated transcripts after infection with common Gram-negative (G-) and -positive (G+) bacteria [32, 34], pathogenic G- bacterial wasps [33, 35, 49] and nematodes (this work) in Drosophila larvae. 381 and 104 transcripts are specifically up- or down-regulated after nematobacterial infection (comprising altogether 485 differentially regulated transcripts in category D).