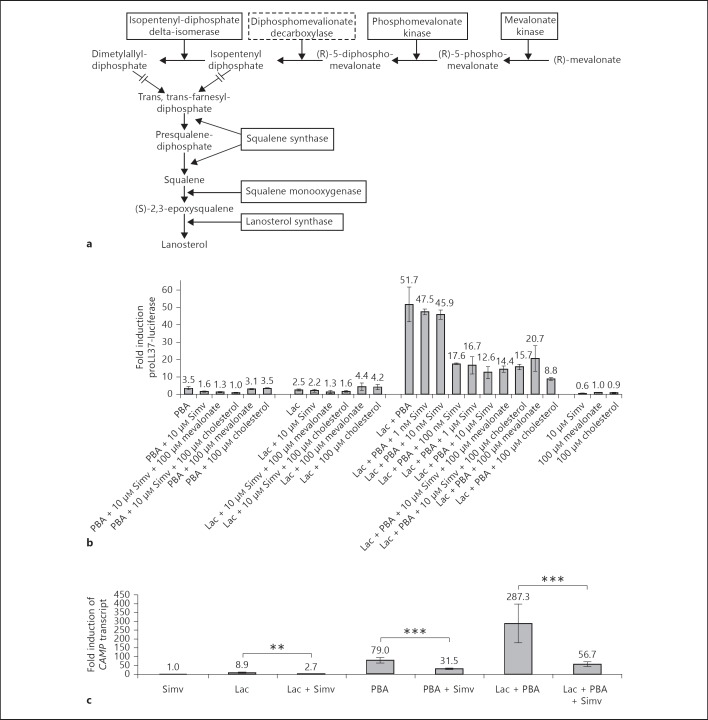
Fig. 4.
a Proteins involved in steroid biosynthesis detected as induced by the proteomic analysis in stimulated HT-29 cells. Closed lines around proteins indicate enzymes that were identified and induced in HT-29 cells treated with lactose or PBA/lactose. Hatched lines indicate proteins not detected in the proteomic analysis. b Screen of the MN8CampLuc cell line using compounds affecting the steroid biosynthesis pathway. Incubation for 24 h of MN8CampLuc cells with an inhibitor to HMG-CoA reductase [simvastatin (Simv) 10 µM] results in an inhibition of the PBA/lactose-mediated synergism on proLL37-luciferase expression. No rescuing effect was observed by administration of either mevalonate or cholesterol in cells incubated with simvastatin. The results are shown as fold induction relative to vehicle control and the data show the mean and SD of at least 4 independent experiments performed in duplicate. c The level of CAMP transcripts in parental HT-29 cells after stimulation with inhibitors of steroid biosynthesis. HT-29 cells incubated with lactose, and/or PBA or PBA/lactose with 10 µM simvastatin (Simv) for 24 h. The results are shown as fold induction relative to vehicle control and the data show the mean and SEM of at least 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. ** p ≤ 0.005; *** p ≤ 0.001.