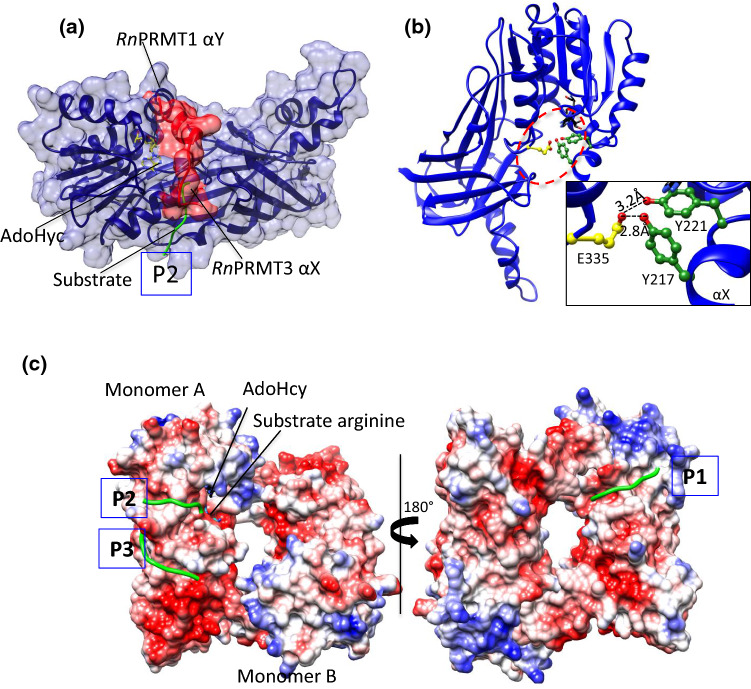
Fig. 3.
The active site of PRMTs. aRnPRMT3 is superimposed on RnPRMT1 (blue ribbon and surface view) whose αX helix density is missing in the crystal structure. The N terminus of αX helix surface residues 208–222 (red ribbon and surface view) from RnPRMT3 occludes the P2 peptidyl arginine entry (green coil). The AdoHcy (stick form) are shown in yellow. P2 is one of the three-substrate entry channels based on the structure of the RnPRMT1–AdoHcy–peptide complex. bRnPRMT2–AdoHyc complex (PDB ID: 1F3L) shows H bonding between the αX helix (green) and the second glutamic acid (yellow) of the double-E loop. AdoHcy is shown in black. Interaction details are shown in zoomed boxes. All H bond interactions are labeled. c The electrostatic surface potential of the RnPRMT1–R3 dimer peptide complex (PDB ID: 1OR8) shows three peptide entry channels: P1 (close to the methionine moiety of AdoHcy), P2 (close to the adenine moiety of AdoHcy) and P3 (on the β-barrel). The peptide backbone is shown as green coil