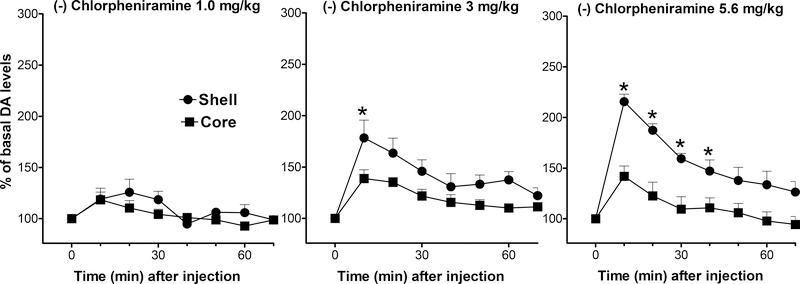
Figure 4.
Dose-dependent effects of intravenous (−)-Chlorpheniramine (1.0, 3.0, and 5.6 mg/kg) administration on extracellular DA levels in dialysates from rats implanted with microdialysis probes in the NAc shell (filled circles) and core (filled squares). Data are expressed as % of basal DA values. *= P<0.05 compared to the corresponding time point in the core. Note that though (−)-Chlorpheniramine has a 16 fold lower affinity for H1 receptors compared to the (+) enantiomer, it shows a significant stimulation of DA levels, and significantly greater effects on DA levels in the shell compared to the core. Results are means, with vertical bars representing SEM, of the amount of DA in 10-min dialysate samples, expressed as percentage of basal values. Basal DA values (fmoles/sample) and group size (n) were: 49.3 ± 7.5 (4), 43.2 ± 5.0 (5), and 39.5 ± 5.1 (5) for 1, 3, and 5.6 mg /kg groups in the NAc shell, and 50.6 ± 2.7 (4), 53.6 ± 5.5 (5), and 40.5 ± 6.7 (5) for 1, 3, and 5.6 mg/kg in the NAc core. *= P<0.05 compared to the corresponding time point in the core.