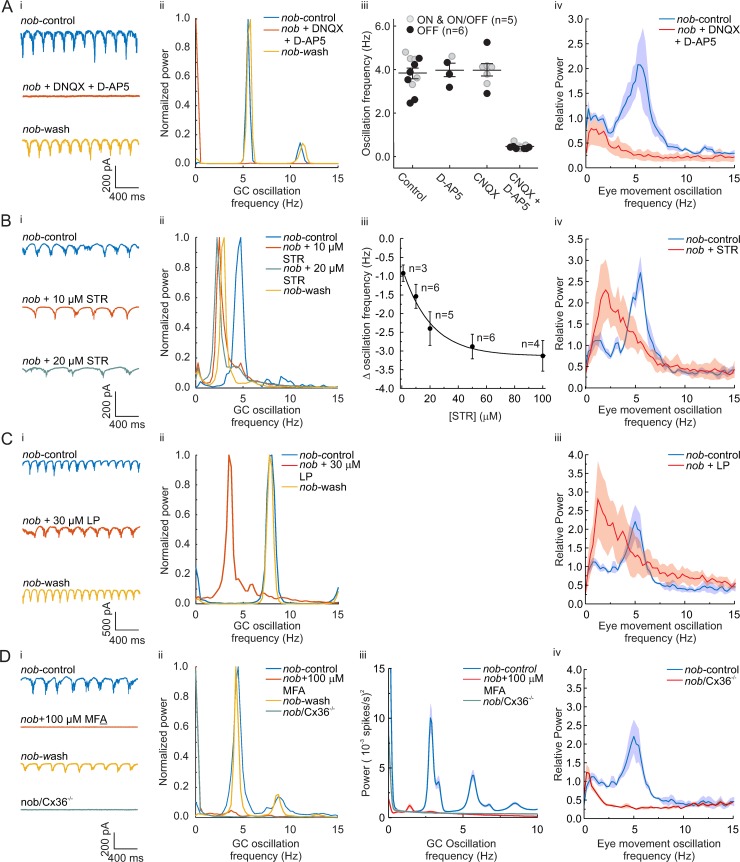
Fig 4. Pharmacological block of excitatory and inhibitory inputs in nob retina blocks or modify both GC and eye-movement oscillations.
(Ai) Oscillating excitatory currents of nob ON-DSGCs (top) are blocked by a cocktail of 50 μM DNQX and 10 μM D-AP5 (middle) and return after washout (bottom). (Aii) The power spectral density plot of the data in (Ai) shows that DNQX/D-AP5 eliminates the 5-Hz oscillating excitatory current. This was found in all nob GCs tested (n = 5). (Aiii) CNQX or D-AP5 administered separately do not block excitatory current oscillations, whereas their combination blocks excitatory current oscillations in nob ON-, OFF-, and ON/OFF-GCs and displaced ACs. (Aiv) Oscillating eye movements in awake nob mice (n = 5) are blocked by intravitreal injections of DNQX/D-AP5 (red; control: blue). (Bi and Bii) STR reduces the oscillation frequency of nob ON-DSGCs excitatory currents. (Biii) Mean data (± SEM) shows that STR consistently reduced the oscillation frequency in a dose-dependent manner. (Biv) Mean (± SEM) power spectral density plots (n = 3) show that intraocular injection of STR reduced the eye-movement oscillation frequency in nob mice. (Ci) Bath application of LP reduced the oscillation frequency of nob ON-DSGCs excitatory currents. (Cii) The power spectral density plots of the ON-DSGC, shown in (Ci), show a shift in peak oscillation frequency to lower frequencies. This was found in all nob GCs tested (n = 6). (Ciii) Mean (± SEM) power spectral density plots (n = 3) show that intraocular injection of LP reduced the frequency of oscillating eye movements in nob mice. (Di) Bath application of MFA blocks the oscillations of nob ON-DSGCs excitatory currents and oscillations are absent in nob/Cx36−/− animals (green trace). (Dii) The power spectral density plots of the ON-DSGC, shown in (Di), show the blocking of oscillations (red trace). This was found in all nob GCs tested (n = 6). Oscillations were absent in all 7 nob/Cx36−/− animals tested. (Diii) Mean (± SEM) power spectra of the spiking activity of nob GCs recorded on the MEA in control (blue trace n = 90) and 100 μM MFA (red trace, n = 98) conditions and in nob/Cx36−/− GCs (green trace, n = 56). (Div) Mean (± SEM) power spectral density plots (n = 3) show that nob/Cx36−/− mice do not show oscillating eye movements. All GC recordings were done in the dark. For the experiments shown in (Aiv, Biv, Ciii, and Div), the stimulus was a stationary sinusoidal grating with a spatial frequency of 0.1 cycles/deg and 100% contrast. The data underlying this figure can be found at https://figshare.com/account/home#/projects/65990. AC, amacrine cell; CNQX, 6-Cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2, 3-dione; Cx36, connexin 36; GC, ganglion cell; D-AP5, D(−)-2-Amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid; DNQX, 6, 7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione; LP, linopiridine hydrochloride; MEA, multielectrode array; MFA, meclofenamic acid; ON-DSGC, ON direction-selective GC; STR, strychnine.