Fig. 1.
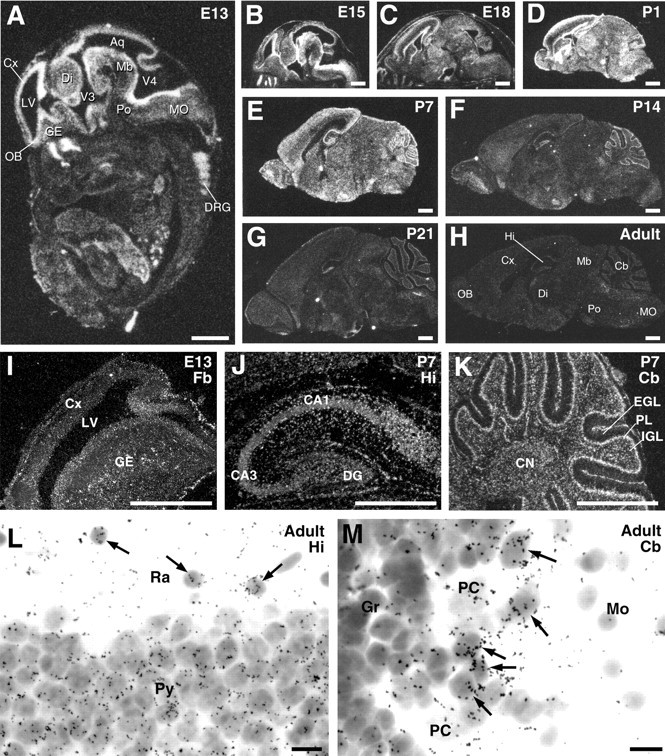
In situ hybridization for ASCT1 mRNA in the developing mouse brain. A–H, Negative images made from x-ray film autoradiograms of parasagittal brain sections at E13 (A), E15 (B), E18 (C), P1 (D), P7 (E), P14 (F), P21 (G), and adult (H). I–K, Enlarged dark-field images by emulsion microautoradiography in the forebrain (Fb) at E13 (I), hippocampus (Hi) at P7 (J), and cerebellum (Cb) at P7 (K).L, M, Bright-field images of the adult hippocampal CA1 (L) and cerebellar cortex (M), in which non-neuronal cells expressing ASCT1 mRNA are indicated by arrows.Aq, Cerebral aqueduct; CA1, CA3, CA1 and CA3 regions of the hippocampus; CN, deep cerebellar nuclei; Cx, cerebral cortex; DG, dentate gyrus; Di, diencephalon; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; EGL, external granular layer;GE, ganglionic eminence; Gr, granular layer; IGL, inner granular layer; LV, lateral ventricle; Mb, midbrain; MO, medulla oblongata; Mo, molecular layer;OB, olfactory bulb; PC, Purkinje cell;PL, Purkinje cell layer; Po, pons;Py, pyramidal cell layer; Ra, stratum radiatum; V3, V4, third and fourth ventricles. Scale bars: A–K, 1 mm; L, M, 10 μm.
