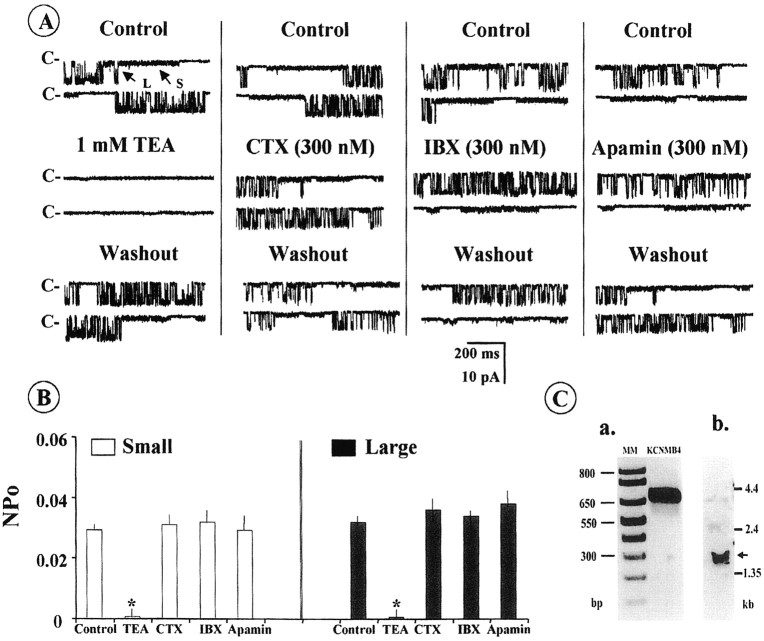
Fig. 4.
Effects of different KCa channel blockers on two types of single-channel KCa currents in outside-out membrane patches of cultured astrocytes recorded using a pipette solution containing 150 mm KCl, 3 mmHEPES, and 0.1 μm Ca2+ at pH 7.2.A, Single-channel KCa currents were recorded from outside-out patches at approximately −70 mV before (control) and after TEA, CTX, IBX, or apamin was added to the bath. External application of TEA (1 mm) reversibly blocked (left) the openings of both the small- and the large-conductance KCa channel currents, whereas the openings of the two types of KCa channel currents were resistant to external application of CTX (300 nm), IBX (300 nm), or apamin (300 nm), as shown in the respective panels. C−, Closed;S, small; L, large.B, Bar graphs depicting a summary of the effects of external application of TEA (1 mm), CTX (300 nm), IBX (300 nm), or apamin (300 nm) on the NPo of the small- and large-conductance KCa single-channel currents recorded from outside-out patches of cultured astrocytes. TEA, but not CTX, IBX, or apamin, reversibly reduced the NPo of the two types of single-channel currents. The asteriskdenotes significant difference (p < 0.05;n = 4–5). C, Detection by RT-PCR (a) and Northern blot analysis (b) of the expression of KCNMB4 transcripts in cultured brain astrocytes. MM, Molecular marker.