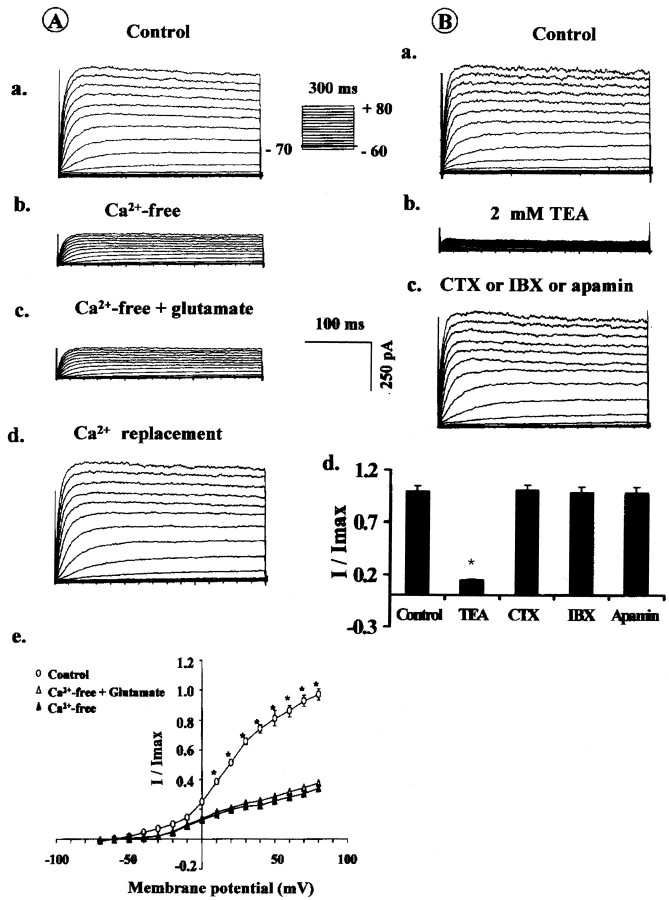
Fig. 5.
A, Effects of low external Ca2+ concentration on the action of glutamate on macroscopic KCa channel current in cultured astrocytes.a, Control outward macroscopic KCa current recorded from cultured astrocytes during step depolarization from −60 to 80 mV in steps of 10 mV increments from a holding potential of −70 mV. b, Lowering external [Ca2+] significantly reduced the magnitude of macroscopic KCacurrents compared with the control (a).c, Application of glutamate (300 μm) to the bath was unable to elicit any effect in low-Ca2+bathing media. Replacement of Ca2+ to the bath restored the magnitude of the macroscopic KCa current to control level (d). e, Line graphs depicting the current–voltage relationship of astrocytic macroscopic KCa current in external bath solution containing a physiological concentration of Ca2+ (open circles), in low-Ca2+ external bath solution (filled triangles), and after addition of glutamate (300 μm, open triangles) to the bath. B, Effects of different KCa channel blockers on macroscopic K+ current recorded from cultured astrocytes. Application of TEA (1 mm) to the bath significantly reduced the macroscopic current (b), whereas addition of 300 nmcharybdotoxin, iberiotoxin, or apamin or 1 mm 4-AP (data not shown) had no effect on the magnitude of the macroscopic KCa current (c) compared with the control (a). d, Bar graphs depicting a summary of the effects of TEA, CTX, IBX, and apamin on the normalized peak macroscopic KCa current recorded from cultured astrocytes. Only application of TEA (1 mm) significantly reduced the macroscopic KCacurrent. The asterisk denotes significant difference (p < 0.05; n = 5 for each group).