Fig. 5.
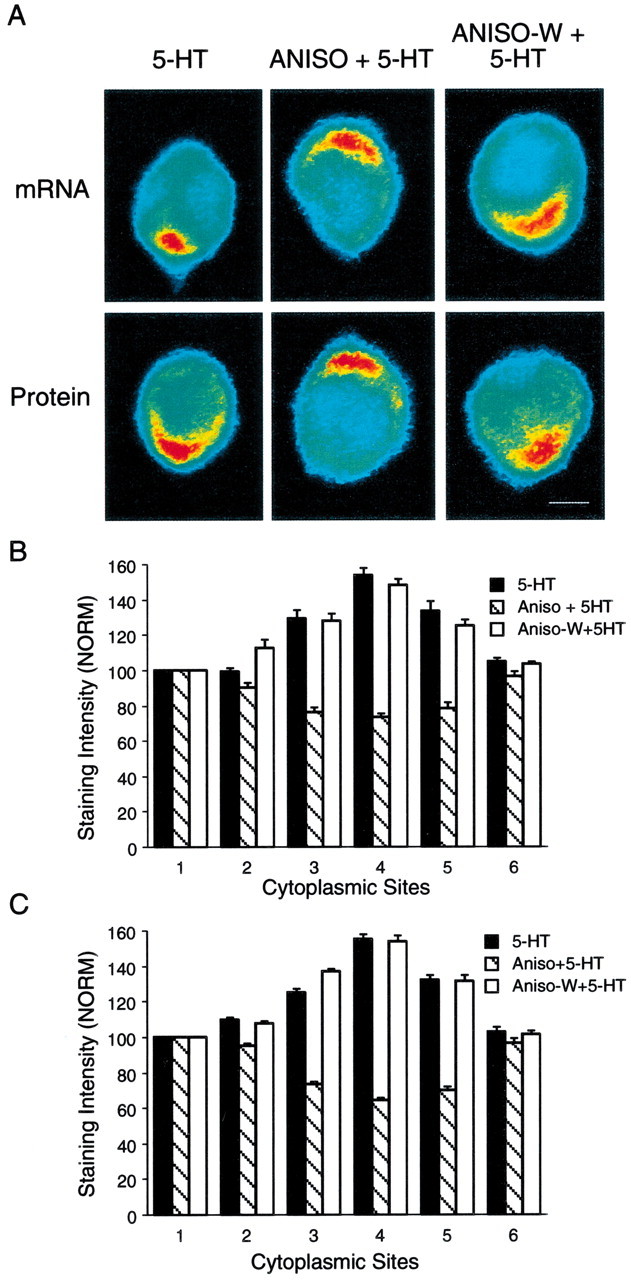
The effects of 5-HT on the distribution of syntaxin mRNA and protein require new protein synthesis.A, The top micrographs are pseudocolor representations of in situ hybridization signals for syntaxin mRNA in SNs cultured with L7 for 5 d and fixed 24 hr after 5-HT (5-HT), 5-HT in the presence of anisomycin (ANISO + 5-HT), or 5-HT 3 hr after washout of anisomycin (ANISO-W + 5-HT). Thebottom micrographs are pseudocolor representations of immunocytochemical signals for syntaxin in SNs 24 hr after the same treatments. The accumulation of syntaxin mRNA and protein in the region of the axon hillock is blocked when 5-HT is applied in the presence of anisomycin. After washout of anisomycin, 5-HT treatment results in mRNA and protein accumulation in the region of the axon hillock. Scale bar, 25 μm. B, C, The histograms summarize the effects of anisomycin on 5-HT producing changes in the distribution of syntaxin mRNA (B) and protein (C). The height of each bar is the mean ± SEM from 7–10 cultures for each treatment in each assay. An ANOVA (two-factor) indicated a significant difference in the signal intensity for syntaxin mRNA (df = 10, 120; F = 30.258;p < 0.001) and protein (df = 10,90;F = 54.955; p < 0.001). Treatment with 5-HT in the presence of anisomycin resulted in significantly lower expression 24 hr later at positions3, 4, and 5 (4–8 o'clock) of syntaxin mRNA (B) compared with 5-HT alone (F values from 13.303 to 16.074;p < 0.01) or 5-HT applied after anisomycin washout (F values from 14.139 to 14.689; p< 0.01). Treatment with 5-HT in the presence of anisomycin also resulted in significantly lower expression of syntaxin (C) at positions 3,4, and 5 (4–8 o'clock) compared with 5-HT alone (F values from 17.174 to 21.943;p < 0.01) or 5-HT applied after anisomycin washout (F values from 16.748 to 21.908).
