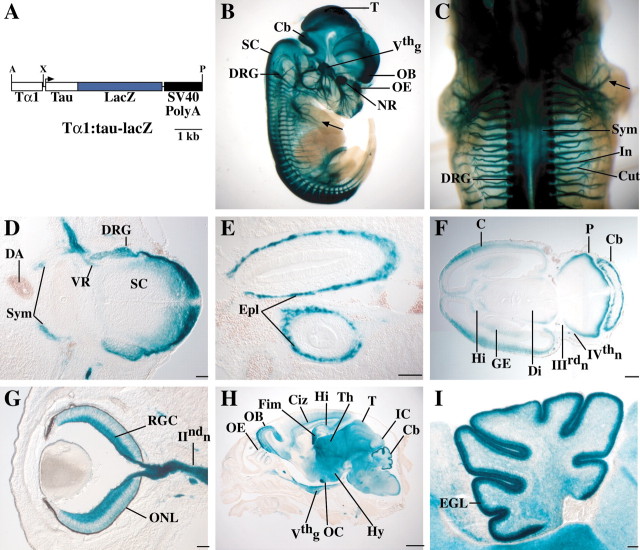
Fig. 1.
A, Diagram of theTα1:tau-lacZ transgenic construct used to generate Tattler-4 mice. The tau-lacZ reporter fusion is expressed under the control of theTα1 α-tubulinpromoter. A polyadenylation signal from SV40 is included in the construct. A, AscI; X,XhoI; P, PmeI.B-I, Tα1:tau-lacZexpression in Tattler-4 transgenic mice. Expression was visualized by X-gal staining, as detailed in Materials and Methods. B, Sagittal view of E13.5 Tattler-4 transgenic embryo stained with X-gal. Staining is present in the neural retina (NR), olfactory epithelium (OE), olfactory bulb (OB), tectum (T), cerebellum (Cb), dorsal spinal cord (SC), trigeminal ganglion (Vthg), and dorsal root ganglia (DRG). Sensory nerves in the limb (arrow) are also stained. C, Dorsal view of E13.5 embryo. The sympathetic chain (Sym) underlying the spinal cord, dorsal root ganglia (DRG), cutaneous (Cut), and intercostal (In) spinal nerves are stained. D, Transverse section through the spinal cord of an E13.5 embryo. Staining is present in the dorsal spinal cord (SC) and dorsal root ganglia (DRG) as well as in the sympathetic chain (Sym). Staining in the ventral root (VR) likely represents preganglionic sympathetic axons, because the ventral horn motor neurons are not stained. The dorsal aorta (DA) is labeled for reference (dorsal is at the right). E, Horizontal section through the abdomen of an E13.5 embryo. Staining is present in the enteric plexus (Epl) of the developing gut.F, Horizontal section through the head of an E13.5 embryo stained in whole mount. Staining is present at the margin of the cerebral cortex (C), pons (P), cerebellum (Cb), diencephalon (Di), ganglionic eminence (GE), and hippocampus (Hi). The oculomotor (IIIrdn) and trochlear (IVthn) cranial nerves are also stained. G, Horizontal section through the eye of an E16.5 embryo. Prominent staining is present in the retinal ganglion cells (RGC) and their axons in the optic nerve (IIndn). Some staining in the developing outer nuclear layer (ONL) is also apparent. H, Parasagittal section through the head of a P0 animal. Staining is present in the OE,OB, intermediate zone of the cerebral cortex (Ciz), hippocampus (Hi), fimbria (Fim), thalamus (Th), optic chiasm (OC), hypothalamus (Hy), tectum (T), inferior colliculus (IC), cerebellum (Cb), and trigeminal ganglion (Vthg).I, Parasagittal section through the cerebellum of a P0 Tattler-4 mouse. Staining is present in cells of the external granule layer (EGL). Scale bars: D,E, G, I, 100 μm;F, 300 μm; H, 1 mm.