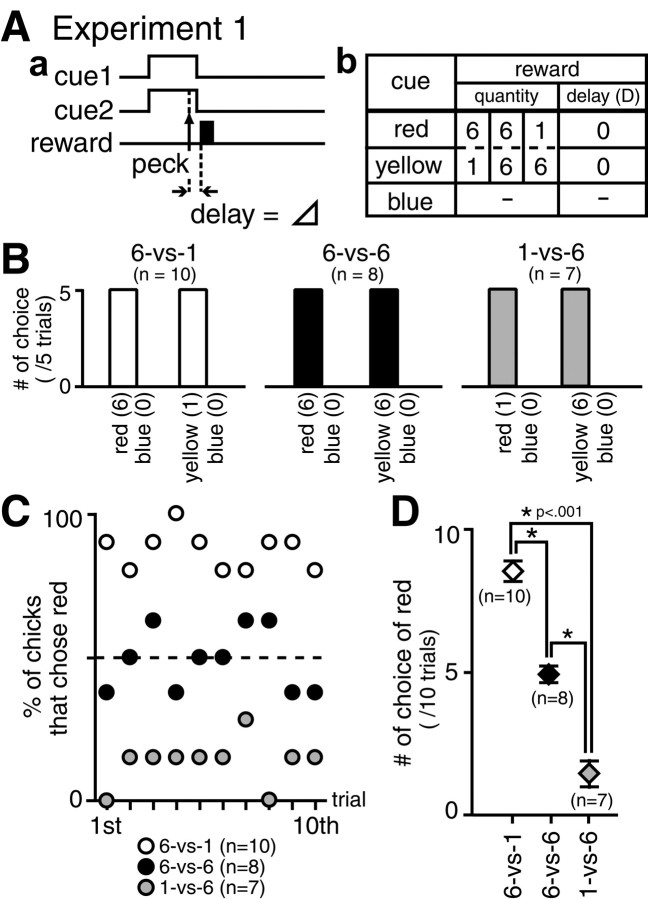
Fig. 1.
Procedure and results of experiment 1.A, Protocol of the choice task with different reward quantities. In training, three types of trials were given in pseudorandom sequences: trials with a pair of identical blue beads (−, no reward), trials with a pair of yellow (1 or 6 pellets) and blue (−, no reward) beads, and trials with a pair of red (6 or 1 pellets) and blue (−, no reward) beads. The side of presentation was randomized. Chicks thus learned to choose a rewarding color (red or yellow) in the red/blue and the yellow/blue trials and not to peck beads in the blue/blue trials. Chicks were then tested in four trial types that were arranged randomly, i.e., blue/blue (20 trials), yellow/blue (5 trials), red/blue (5 trials), and red/yellow (10 trials). The side of presentation was also randomized. B, Number of choices in test trials with red/blue pair and yellow/blue pair; data obtained from the 6-vs-1 chicks (open columns), the 6-vs-6 chicks (filled columns), and the 1-vs-6 chicks (shaded columns). The number of choices per five trials was averaged over chicks. All of the chicks chose red or yellow;n denotes number of chicks. C, Proportion (percentage) of chicks that chose red was plotted along the 10 test trials with red/yellow pairs. Data were obtained from the 6-vs-1 chicks (open symbols), the 6-vs-6 chicks (filled symbols), and the 1-vs-6 chicks (shaded symbols). D, The number of choices of red was counted in the red/yellow test trials, averaged over chicks, and compared among 6-vs-1, 6-vs-6, and 1-vs-6 chicks; post hoc multiple comparisons between pairs among these three groups revealed significant differences at p < 0.001 (asterisks). Error bars denote SEM.